Page 195 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 195
LOGIC GATE
All binary digital devices and systems employ electronic switches that per-
form various Boolean functions. A switch of this type is called a logic gate.
Usually, the binary digit 1 stands for “true”and is represented by about
+5 V. The binary digit 0 stands for “false” and is represented by a voltage
near 0 V. This scheme is known as positive logic. There are other logic
forms, the most common of which is negative logic (in which the digit 1 is
represented by a more negative voltage than the digit 0). The remainder
of this discussion deals with positive logic. Logic Gate
An inverter, also called a NOT gate, has one input and one output. It
reverses the state of the input. An OR gate can have two or more inputs.
If both, or all, of the inputs are 0, then the output is 0. If any of the in-
puts are 1, then the output is 1.An AND gate can have two or more inputs.
If both, or all, of the inputs are 1, then the output is 1. Otherwise the
output is 0.
Sometimes an inverter and an OR gate are combined. This produces a
NOR gate. If an inverter and an AND gate are combined, the result is a
NAND gate. An exclusive OR gate, also called an XOR gate, has two inputs
and one output. If the two inputs are the same (either both 1 or both 0),
then the output is 0. If the two inputs are different, then the output is 1.
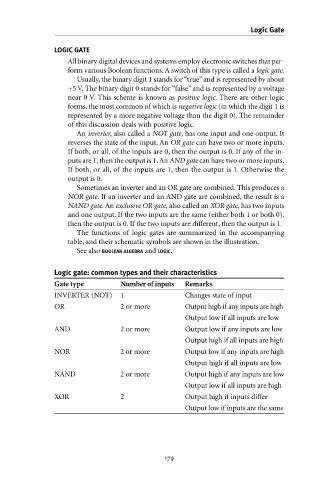
The functions of logic gates are summarized in the accompanying
table, and their schematic symbols are shown in the illustration.
See also BOOLEAN ALGEBRA and LOGIC.
Logic gate: common types and their characteristics
Gate type Number of inputs Remarks
INVERTER (NOT) 1 Changes state of input
OR 2 or more Output high if any inputs are high
Output low if all inputs are low
AND 2 or more Output low if any inputs are low
Output high if all inputs are high
NOR 2 or more Output low if any inputs are high
Output high if all inputs are low
NAND 2 or more Output high if any inputs are low
Output low if all inputs are high
XOR 2 Output high if inputs differ
Output low if inputs are the same