Page 192 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 192
Legged Locomotion
In a fiber-optic laser-communications system, the beam is guided
through a glass or plastic filament. This is similar to wire or cable commu-
nications, but with far more versatility. Optical systems are not susceptible
to the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI), as are some wire and
cable networks. Fiber-optic systems lend themselves well to robot control,
especially in hostile environments such as the deep sea.Compare MICROWAVE
DATA TRANSMISSION.
LEGGED LOCOMOTION
See ROBOT LEG.
LINEAR PROGRAMMING
Linear programming is a process of optimizing two or more variables that
change independently of one another.
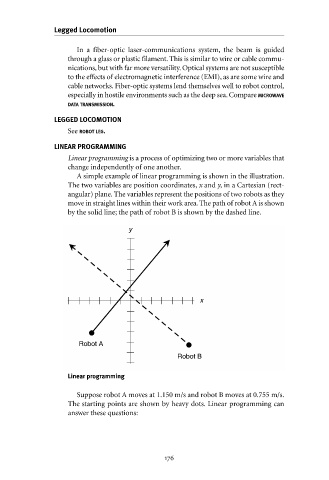
A simple example of linear programming is shown in the illustration.
The two variables are position coordinates, x and y, in a Cartesian (rect-
angular) plane. The variables represent the positions of two robots as they
move in straight lines within their work area. The path of robot A is shown
by the solid line; the path of robot B is shown by the dashed line.
y
x
Robot A
Robot B
Linear programming
Suppose robot A moves at 1.150 m/s and robot B moves at 0.755 m/s.
The starting points are shown by heavy dots. Linear programming can
answer these questions: