Page 242 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 242
Pitch
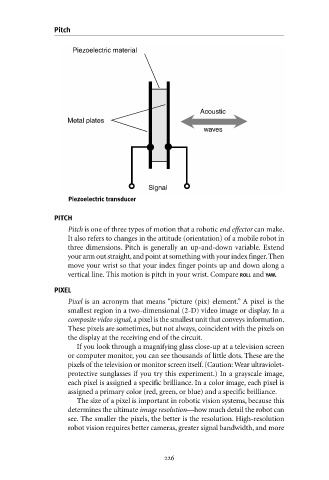
Piezoelectric material
Metal plates Acoustic
waves
Signal
Piezoelectric transducer
PITCH
Pitch is one of three types of motion that a robotic end effector can make.
It also refers to changes in the attitude (orientation) of a mobile robot in
three dimensions. Pitch is generally an up-and-down variable. Extend
your arm out straight,and point at something with your index finger.Then
move your wrist so that your index finger points up and down along a
vertical line. This motion is pitch in your wrist. Compare ROLL and YAW.
PIXEL
Pixel is an acronym that means “picture (pix) element.” A pixel is the
smallest region in a two-dimensional (2-D) video image or display. In a
composite video signal, a pixel is the smallest unit that conveys information.
These pixels are sometimes, but not always, coincident with the pixels on
the display at the receiving end of the circuit.
If you look through a magnifying glass close-up at a television screen
or computer monitor, you can see thousands of little dots. These are the
pixels of the television or monitor screen itself. (Caution: Wear ultraviolet-
protective sunglasses if you try this experiment.) In a grayscale image,
each pixel is assigned a specific brilliance. In a color image, each pixel is
assigned a primary color (red, green, or blue) and a specific brilliance.
The size of a pixel is important in robotic vision systems, because this
determines the ultimate image resolution—how much detail the robot can
see. The smaller the pixels, the better is the resolution. High-resolution
robot vision requires better cameras, greater signal bandwidth, and more