Page 243 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 243
Point-to-Point Motion
memory than low-resolution robot vision. High-resolution systems also
cost more than low-resolution systems.
See also COMPOSITE VIDEO SIGNAL, RESOLUTION, and VISION SYSTEM.
PLAN/SENSE/ACT
See HIERARCHICAL PARADIGM, HYBRID DELIBERATIVE/REACTIVE PARADIGM, and REACTIVE PARADIGM.
PNEUMATIC DRIVE
A pneumatic drive is a method of providing movement to a robot manip-
ulator. It uses compressed gas, such as air, to transfer forces to various
joints, telescoping sections, and end effectors.
The pneumatic drive consists of a power supply, one or more motors,
a set of pistons and valves, and a feedback loop. The valves and pistons
control the movement of the gas. Because the gas is compressible, the
drive cannot impart large forces without significant positioning errors. A
feedback loop consists of one or more force sensors that can provide
error correction and help the manipulator follow its intended path.
Pneumatically driven manipulators are used when precision and
speed are not critical. Compare HYDRAULIC DRIVE.
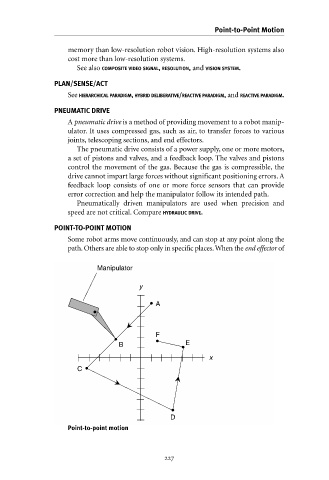
POINT-TO-POINT MOTION
Some robot arms move continuously, and can stop at any point along the
path. Others are able to stop only in specific places.When the end effector of
Manipulator
y
A
F
B E
x
C
D
Point-to-point motion