Page 244 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 244
Polar Coordinate Geometry
a robot arm can attain only certain positions,the manipulator is said to em-
ploy point-to-point motion. The illustration shows point-to-point motion in
which six stopping points, called via points, are possible (A through F).
In some robots that use point-to-point motion, the controller stores a
large number of via points within the work envelope of the manipulator.
These points are so close together that the resulting motion is continuous
for practical purposes. Small time increments are used, such as 0.01 s or
0.001 s. This scheme is the robot-motion analog of bit-map computer
graphics. Compare CONTINUOUS-PATH MOTION.
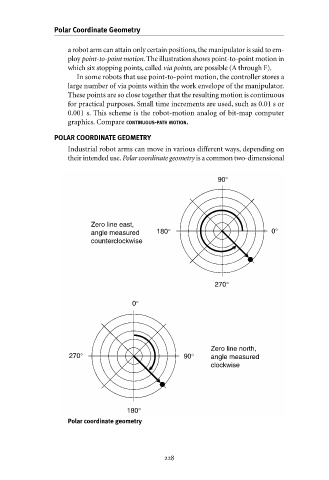
POLAR COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Industrial robot arms can move in various different ways, depending on
their intended use.Polar coordinate geometry is a common two-dimensional
90°
Zero line east,
angle measured 180° 0°
counterclockwise
270°
0°
Zero line north,
270° 90° angle measured
clockwise
180°
Polar coordinate geometry