Page 364 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 364
Yaw
demonstrate how robots work, and that there is no miracle involved in
their functioning.
The XR robots were introduced during the 1980s, and sold for less
than $3000 each. They did various tasks with high precision, and used a
programming device similar to a teach box. For tasks involving numerous
steps to be carried out in specific order, a personal computer could be used
as the robot controller.
The XR robots proved useful as teaching aids in corporations and
schools. Many people get uneasy around robots, especially the program-
mable type. The XR robots helped rid people of the fears they sometimes
have about robots.
See also EDUCATIONAL ROBOT, ROBOT ARM, and TEACH BOX.
YAW
Yaw is one of three types of motion that a robotic end effector can make.
Extend your arm out straight, and point at something with your index
finger. Then move your wrist so that your index finger points back and
forth (to the left and right) in a horizontal plane. This motion is yaw in
your wrist. Compare PITCH and ROLL.
Y AXIS
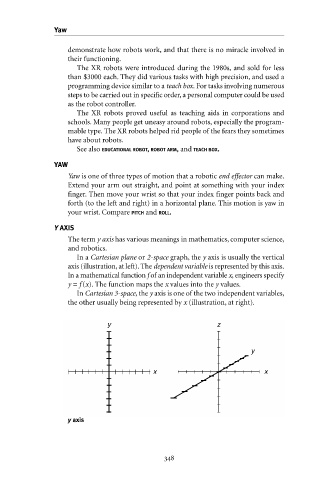
The term y axis has various meanings in mathematics, computer science,
and robotics.
In a Cartesian plane or 2-space graph, the y axis is usually the vertical
axis (illustration, at left). The dependent variable is represented by this axis.
In a mathematical function f of an independent variable x, engineers specify
y = f (x). The function maps the x values into the y values.
In Cartesian 3-space, the y axis is one of the two independent variables,
the other usually being represented by x (illustration, at right).
y z
y
x x
y axis