Page 410 - Construction Waterproofing Handbook
P. 410
10.12 CHAPTER TEN
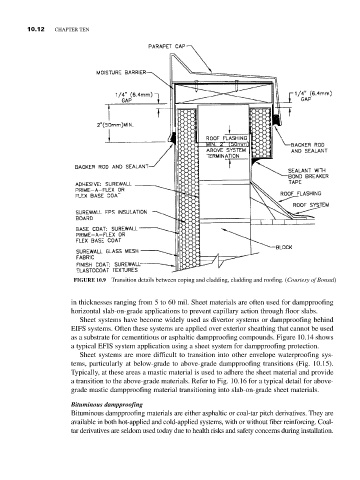
FIGURE 10.9 Transition details between coping and cladding, cladding and roofing. (Courtesy of Bonsal)
in thicknesses ranging from 5 to 60 mil. Sheet materials are often used for dampproofing
horizontal slab-on-grade applications to prevent capillary action through floor slabs.
Sheet systems have become widely used as divertor systems or dampproofing behind
EIFS systems. Often these systems are applied over exterior sheathing that cannot be used
as a substrate for cementitious or asphaltic dampproofing compounds. Figure 10.14 shows
a typical EFIS system application using a sheet system for dampproofing protection.
Sheet systems are more difficult to transition into other envelope waterproofing sys-
tems, particularly at below-grade to above-grade dampproofing transitions (Fig. 10.15).
Typically, at these areas a mastic material is used to adhere the sheet material and provide
a transition to the above-grade materials. Refer to Fig. 10.16 for a typical detail for above-
grade mastic dampproofing material transitioning into slab-on-grade sheet materials.
Bituminous dampproofing
Bituminous dampproofing materials are either asphaltic or coal-tar pitch derivatives. They are
available in both hot-applied and cold-applied systems, with or without fiber reinforcing. Coal-
tar derivatives are seldom used today due to health risks and safety concerns during installation.