Page 237 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 237
218 Control theory in biomedical engineering
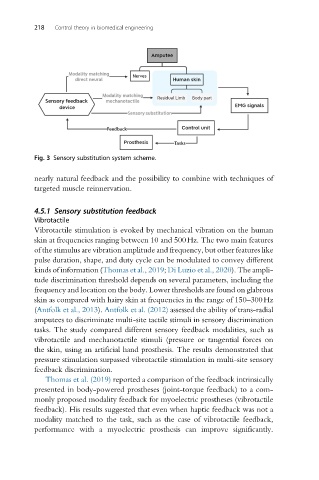
Fig. 3 Sensory substitution system scheme.
nearly natural feedback and the possibility to combine with techniques of
targeted muscle reinnervation.
4.5.1 Sensory substitution feedback
Vibrotactile
Vibrotactile stimulation is evoked by mechanical vibration on the human
skin at frequencies ranging between 10 and 500Hz. The two main features
of the stimulus are vibration amplitude and frequency, but other features like
pulse duration, shape, and duty cycle can be modulated to convey different
kinds of information (Thomas et al., 2019; Di Luzio et al., 2020). The ampli-
tude discrimination threshold depends on several parameters, including the
frequency and location on the body. Lower thresholds are found on glabrous
skin as compared with hairy skin at frequencies in the range of 150–300Hz
(Antfolk et al., 2013). Antfolk et al. (2012) assessed the ability of trans-radial
amputees to discriminate multi-site tactile stimuli in sensory discrimination
tasks. The study compared different sensory feedback modalities, such as
vibrotactile and mechanotactile stimuli (pressure or tangential forces on
the skin, using an artificial hand prosthesis. The results demonstrated that
pressure stimulation surpassed vibrotactile stimulation in multi-site sensory
feedback discrimination.
Thomas et al. (2019) reported a comparison of the feedback intrinsically
presented in body-powered prostheses (joint-torque feedback) to a com-
monly proposed modality feedback for myoelectric prostheses (vibrotactile
feedback). His results suggested that even when haptic feedback was not a
modality matched to the task, such as the case of vibrotactile feedback,
performance with a myoelectric prosthesis can improve significantly.