Page 91 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 91
Adaptive control of artificial pancreas systems for treatment of type 1 diabetes 77
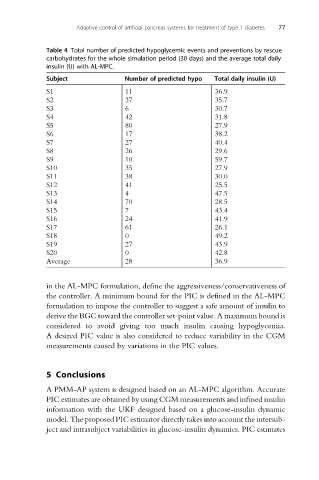
Table 4 Total number of predicted hypoglycemic events and preventions by rescue
carbohydrates for the whole simulation period (30 days) and the average total daily
insulin (U) with AL-MPC.
Subject Number of predicted hypo Total daily insulin (U)
S1 11 36.9
S2 37 35.7
S3 6 30.7
S4 42 31.8
S5 80 27.9
S6 17 38.2
S7 27 40.4
S8 26 29.6
S9 10 59.7
S10 35 27.9
S11 38 30.0
S12 41 25.5
S13 4 47.5
S14 70 28.5
S15 7 43.4
S16 24 41.9
S17 61 26.1
S18 0 49.2
S19 27 43.9
S20 0 42.8
Average 28 36.9
in the AL-MPC formulation, define the aggressiveness/conservativeness of
the controller. A minimum bound for the PIC is defined in the AL-MPC
formulation to impose the controller to suggest a safe amount of insulin to
derive the BGC toward the controller set-point value. A maximum bound is
considered to avoid giving too much insulin causing hypoglycemia.
A desired PIC value is also considered to reduce variability in the CGM
measurements caused by variations in the PIC values.
5 Conclusions
A PMM-AP system is designed based on an AL-MPC algorithm. Accurate
PIC estimates are obtained by using CGM measurements and infused insulin
information with the UKF designed based on a glucose-insulin dynamic
model. The proposed PIC estimator directly takes into account the intersub-
ject and intrasubject variabilities in glucose-insulin dynamics. PIC estimates