Page 286 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 286
260 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 261
In recent years, many owners of large-diameter transmission and
distribution piping systems typically have protected their investment
by installing pipe with internal linings, by cleaning and lining pipe in
place, or by adding a cathodic protection system for external corrosion
(see Chap. 13 for some examples). However, there are still many
thousands of kilometers of unlined metallic piping in use throughout
North America and Europe. Costs to maintain operability over and
above the normal accrue when this piping must be replaced
prematurely or cleaned and lined in place.
Environmental Concerns
Corrosion of water distribution piping raises environmental concerns
mostly due to the presence of lead, cadmium, zinc, and copper in
drinking water. These metals enter the wastewater collection system
and eventually accumulate in the sludge and end up in a landfill, on
croplands, or other locations, depending on the disposal method.
Metals corroded from water piping are the largest source of these
contaminants in the wastewater of many communities.
8.2.2 Corrosion Management
System reliability is of the utmost importance to water suppliers and
their customers. However, corrosion problems can vary greatly
within a single system because many variables affect corrosion, for
example, pipe material, pipe age, pipe wall thickness, water additives,
corrosion inhibitor treatment, soil chemistry, soil moisture content
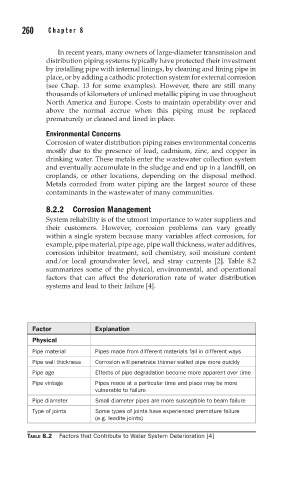
and/or local groundwater level, and stray currents [2]. Table 8.2
summarizes some of the physical, environmental, and operational
factors that can affect the deterioration rate of water distribution
systems and lead to their failure [4].
Factor Explanation
Physical
Pipe material Pipes made from different materials fail in different ways
Pipe wall thickness Corrosion will penetrate thinner walled pipe more quickly
Pipe age Effects of pipe degradation become more apparent over time
Pipe vintage Pipes made at a particular time and place may be more
vulnerable to failure
Pipe diameter Small diameter pipes are more susceptible to beam failure
Type of joints Some types of joints have experienced premature failure
(e.g. leadite joints)
TABLE 8.2 Factors that Contribute to Water System Deterioration [4]