Page 293 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 293
C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 267
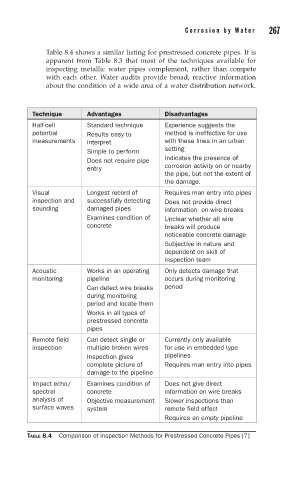
Table 8.4 shows a similar listing for prestressed concrete pipes. It is
apparent from Table 8.3 that most of the techniques available for
inspecting metallic water pipes complement, rather than compete
with each other. Water audits provide broad, reactive information
about the condition of a wide area of a water distribution network.
Technique Advantages Disadvantages
Half-cell Standard technique Experience suggests the
potential Results easy to method is ineffective for use
measurements interpret with these lines in an urban
Simple to perform setting
Does not require pipe Indicates the presence of
entry corrosion activity on or nearby
the pipe, but not the extent of
the damage.
Visual Longest record of Requires man entry into pipes
inspection and successfully detecting Does not provide direct
sounding damaged pipes information on wire breaks
Examines condition of Unclear whether all wire
concrete breaks will produce
noticeable concrete damage
Subjective in nature and
dependent on skill of
inspection team
Acoustic Works in an operating Only detects damage that
monitoring pipeline occurs during monitoring
Can detect wire breaks period
during monitoring
period and locate them
Works in all types of
prestressed concrete
pipes
Remote field Can detect single or Currently only available
inspection multiple broken wires for use in embedded type
Inspection gives pipelines
complete picture of Requires man entry into pipes
damage to the pipeline
Impact echo/ Examines condition of Does not give direct
spectral concrete information on wire breaks
analysis of Objective measurement Slower inspections than
surface waves system remote field effect
Requires an empty pipeline
TABLE 8.4 Comparison of Inspection Methods for Prestressed Concrete Pipes [7]