Page 311 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 311
282 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 283
2−
2+
Where (Ca ) and (CO ) are the molalities of the Ca and CO
2+
2−
3
3
ions, respectively, and K sp, aragonite is the solubility product of aragonite
(at 25°C K sp, aragonite = 6.7 × 10 )
−7
In order to understand the buildup of carbonate ions at a metallic
surface under cathodic protection (CP), one can consider the simplified
electrochemical production of carbonate ions described in Eq. (8.13) that
summarizes the effect of CP in the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide.
−
2−
H O + CO + 2e → H + CO 3 (8.13)
2
2
2
An expression for the limiting current corresponding to this
reaction is described in Eq. (8.14).
2− − C
C surface bulk
i = nFD CO 3 CO 3 2− (8.14)
L CO 3 2− δ
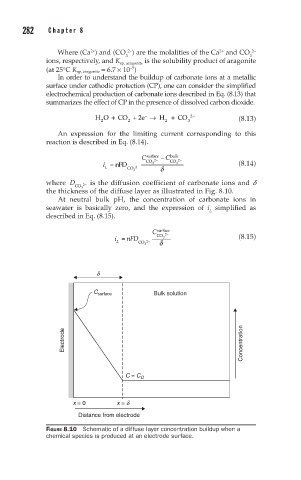
where D 2− is the diffusion coefficient of carbonate ions and d
CO 3
the thickness of the diffuse layer as illustrated in Fig. 8.10.
At neutral bulk pH, the concentration of carbonate ions in
seawater is basically zero, and the expression of i simplified as
L
described in Eq. (8.15).
C surface
i = nFD CO 3 2− CO 3 2− (8.15)
δ
L
d
C surface Bulk solution
Electrode Concentration
C = C O
x = 0 x = d
Distance from electrode
FIGURE 8.10 Schematic of a diffuse layer concentration buildup when a
chemical species is produced at an electrode surface.