Page 488 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 488
11.5 Bit-Parallel Arithmetic 473
therefore be shorter than for one with fewer steps. Thus, to accurately estimate
the addition time a detailed analysis and circuit realization are required.
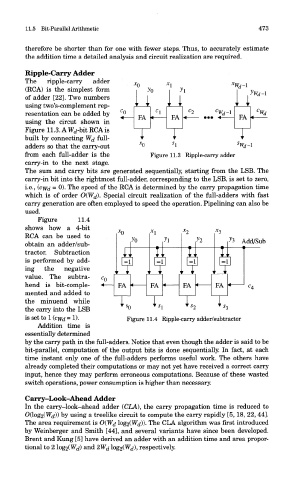
Ripple-Carry Adder
The ripple-carry adder
(RCA) is the simplest form
of adder [22]. Two numbers
using two's-complement rep-
resentation can be added by
using the circut shown in
Figure 11.3. A W d-bit RCA is
built by connecting W^ full-
adders so that the carry-out
from each full-adder is the
carry-in to the next stage.
The sum and carry bits are generated sequentially, starting from the LSB. The
carry-in bit into the rightmost full-adder, corresponding to the LSB, is set to zero,
i.e., (cyfd = 0)- The speed of the RCA is determined by the carry propagation time
which is of order O(W<f). Special circuit realization of the full-adders with fast
carry generation are often employed to speed the operation. Pipelining can also be
used.
Figure 11.4
shows how a 4-bit
RCA can be used to
obtain an adder/sub-
tractor. Subtraction
is performed by add-
ing the negative
value. The subtra-
hend is bit-comple-
mented and added to
the minuend while
the carry into the LSB
is set to 1 (cwd = 1). Figure 11.4 Ripple-carry adder/subtractor
Addition time is
essentially determined
by the carry path in the full-adders. Notice that even though the adder is said to be
bit-parallel, computation of the output bits is done sequentially. In fact, at each
time instant only one of the full-adders performs useful work. The others have
already completed their computations or may not yet have received a correct carry
input, hence they may perform erroneous computations. Because of these wasted
switch operations, power consumption is higher than necessary.
Carry-Look-Ahead Adder
In the carry-look-ahead adder (CLA), the carry propagation time is reduced to
O(log2(W^)) by using a treelike circuit to compute the carry rapidly [5, 18, 22, 44].
The area requirement is O(W d log2(W^)). The CLA algorithm was first introduced
by Weinberger and Smith [44], and several variants have since been developed.
Brent and Rung [5] have derived an adder with an addition time and area propor-
tional to 2 log2(W^) and 2W^ log2(W^), respectively.