Page 177 -
P. 177
11-ch04-125-186-9780123814791
HAN
2011/6/1
140 Chapter 4 Data Warehousing and Online Analytical Processing 3:17 Page 140 #16
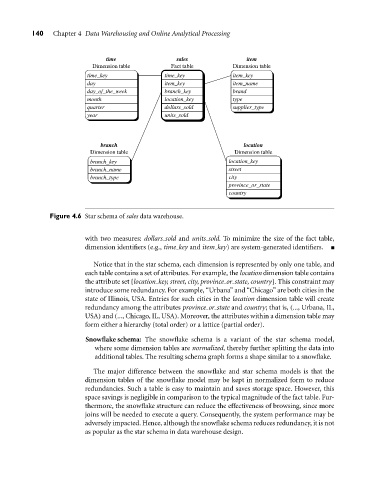
time sales item
Dimension table Fact table Dimension table
time_key time_key item_key
day item_key item_name
day_of_the_week branch_key brand
month location_key type
quarter dollars_sold supplier_type
year units_sold
branch location
Dimension table Dimension table
branch_key location_key
branch_name street
branch_type city
province_or_state
country
Figure 4.6 Star schema of sales data warehouse.
with two measures: dollars sold and units sold. To minimize the size of the fact table,
dimension identifiers (e.g., time key and item key) are system-generated identifiers.
Notice that in the star schema, each dimension is represented by only one table, and
each table contains a set of attributes. For example, the location dimension table contains
the attribute set {location key, street, city, province or state, country}. This constraint may
introduce some redundancy. For example, “Urbana” and “Chicago” are both cities in the
state of Illinois, USA. Entries for such cities in the location dimension table will create
redundancy among the attributes province or state and country; that is, (..., Urbana, IL,
USA) and (..., Chicago, IL, USA). Moreover, the attributes within a dimension table may
form either a hierarchy (total order) or a lattice (partial order).
Snowflake schema: The snowflake schema is a variant of the star schema model,
where some dimension tables are normalized, thereby further splitting the data into
additional tables. The resulting schema graph forms a shape similar to a snowflake.
The major difference between the snowflake and star schema models is that the
dimension tables of the snowflake model may be kept in normalized form to reduce
redundancies. Such a table is easy to maintain and saves storage space. However, this
space savings is negligible in comparison to the typical magnitude of the fact table. Fur-
thermore, the snowflake structure can reduce the effectiveness of browsing, since more
joins will be needed to execute a query. Consequently, the system performance may be
adversely impacted. Hence, although the snowflake schema reduces redundancy, it is not
as popular as the star schema in data warehouse design.