Page 179 -
P. 179
2011/6/1
HAN
11-ch04-125-186-9780123814791
142 Chapter 4 Data Warehousing and Online Analytical Processing 3:17 Page 142 #18
time sales item shipping shipper
Dimension table Fact table Dimension table Fact table Dimension table
time_key time_key item_key item_key shipper_key
day item_key item_name time_key shipper_name
day_of_week branch_key brand shipper_key location_key
month location_key type from_location shipper_type
quarter dollars_sold supplier_type to_location
year units_sold dollars_cost
units_shipped
branch location
Dimension table Dimension table
branch_key location_key
branch_name street
branch_type city
province_or_state
country
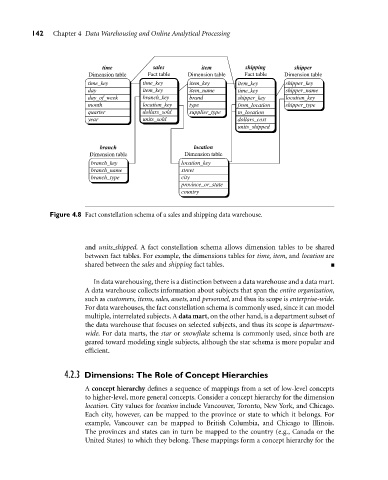
Figure 4.8 Fact constellation schema of a sales and shipping data warehouse.
and units shipped. A fact constellation schema allows dimension tables to be shared
between fact tables. For example, the dimensions tables for time, item, and location are
shared between the sales and shipping fact tables.
In data warehousing, there is a distinction between a data warehouse and a data mart.
A data warehouse collects information about subjects that span the entire organization,
such as customers, items, sales, assets, and personnel, and thus its scope is enterprise-wide.
For data warehouses, the fact constellation schema is commonly used, since it can model
multiple, interrelated subjects. A data mart, on the other hand, is a department subset of
the data warehouse that focuses on selected subjects, and thus its scope is department-
wide. For data marts, the star or snowflake schema is commonly used, since both are
geared toward modeling single subjects, although the star schema is more popular and
efficient.
4.2.3 Dimensions: The Role of Concept Hierarchies
A concept hierarchy defines a sequence of mappings from a set of low-level concepts
to higher-level, more general concepts. Consider a concept hierarchy for the dimension
location. City values for location include Vancouver, Toronto, New York, and Chicago.
Each city, however, can be mapped to the province or state to which it belongs. For
example, Vancouver can be mapped to British Columbia, and Chicago to Illinois.
The provinces and states can in turn be mapped to the country (e.g., Canada or the
United States) to which they belong. These mappings form a concept hierarchy for the