Page 96 -
P. 96
Overview 75
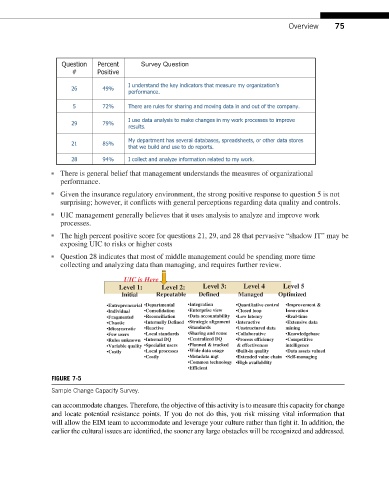
There is general belief that management understands the measures of organizational
performance.
Given the insurance regulatory environment, the strong positive response to question 5 is not
surprising; however, it conflicts with general perceptions regarding data quality and controls.
UIC management generally believes that it uses analysis to analyze and improve work
processes.
The high percent positive score for questions 21, 29, and 28 that pervasive “shadow IT” may be
exposing UIC to risks or higher costs
Question 28 indicates that most of middle management could be spending more time
collecting and analyzing data than managing, and requires further review.
UIC is Here
Level 1: Level 2: Level 3: Level 4 Level 5
Initial Repeatable Defined Managed Optimized
•Entrepreneurial •Departmental •Integration •Quantitative control •Improvement &
•Individual •Consolidation •Enterprise view •Closed loop Innovation
•Fragmented •Reconciliation •Data accountability •Low latency •Real-time
•Chaotic •Internally Defined •Strategic alignment •Interactive •Extensive data
•Idiosyncratic •Reactive •Standards •Unstructured data mining
•Few users •Local standards •Sharing and reuse •Collaborative •Knowledgebase
•Rules unknown •Internal DQ •Centralized DQ •Process efficiency •Competitive
•Variable quality •Specialist users •Planned & tracked & effectiveness intelligence
•Costly •Local processes •Wide data usage •Built-in quality •Data assets valued
•Costly •Metadata mgt •Extended value chain •Self-managing
•Common technology •High availability
•Efficient
FIGURE 7-5
Sample Change Capacity Survey.
can accommodate changes. Therefore, the objective of this activity is to measure this capacity for change
and locate potential resistance points. If you do not do this, you risk missing vital information that
will allow the EIM team to accommodate and leverage your culture rather than fight it. In addition, the
earlier the cultural issues are identified, the sooner any large obstacles will be recognized and addressed.