Page 391 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 391
Maintenance management with application Chapter | 13 353
describes the operating state of the generating units. The variable under
study, as well as the variable “Level,” was transferred to a percentage scale
of 100, where “EXCELLENT” corresponds to the range of maximum values
and the variable “BAD” corresponds to the range of minimum values up to
zero. This value gives a greater range of possibilities, making the case study
more precise. Thus we can deduce that the equation that defines the estima-
tion is. These variables are used for decision-making involving the predis-
patch of the unit generators, as shown in Table 13.6.
13.5 Fuzzy simulation
The fuzzy simulation containing the system variables was performed using
the MATLAB version 8.0 tool, and the fuzzy model applied in this simula-
tion was Mamdani. This model is characterized by adopting the semantic
rules used for the processing of inferences and is commonly referred to as
maximum minimum inference. Such an inference model applies well to this
type of problem since it uses union and intersection operations between sets.
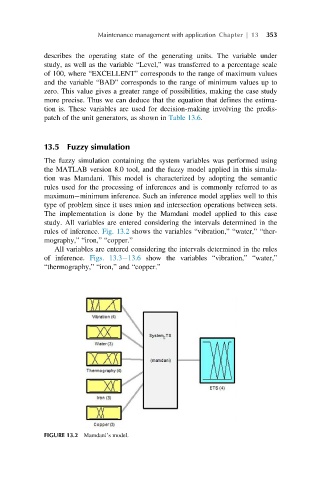
The implementation is done by the Mamdani model applied to this case
study. All variables are entered considering the intervals determined in the
rules of inference. Fig. 13.2 shows the variables “vibration,” “water,” “ther-
mography,” “iron,” “copper.”
All variables are entered considering the intervals determined in the rules
of inference. Figs. 13.3 13.6 show the variables “vibration,” “water,”
“thermography,” “iron,” and “copper.”
FIGURE 13.2 Mamdani’s model.