Page 388 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 388
350 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
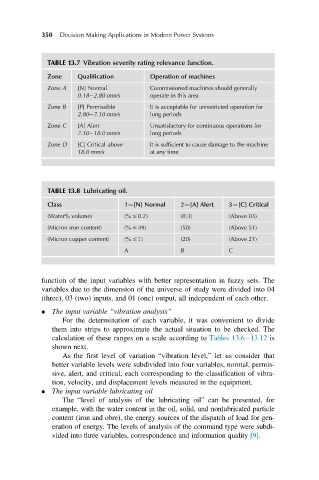
TABLE 13.7 Vibration severity rating relevance function.
Zone Qualification Operation of machines
Zone A [N] Normal Commissioned machines should generally
0.18 2.80 mm/s operate in this area
Zone B [P] Permissible It is acceptable for unrestricted operation for
2.80 7.10 mm/s long periods
Zone C [A] Alert Unsatisfactory for continuous operations for
7.10 18.0 mm/s long periods
Zone D [C] Critical above It is sufficient to cause damage to the machine
18.0 mm/s at any time
TABLE 13.8 Lubricating oil.
Class 1—[N] Normal 2—[A] Alert 3—[C] Critical
(Water% volume) (% # 0.2) (0.3) (Above 03)
(Micron iron content) (% # 49) (50) (Above 51)
(Micron copper content) (% # 1) (20) (Above 21)
A B C
function of the input variables with better representation in fuzzy sets. The
variables due to the dimension of the universe of study were divided into 04
(three), 03 (two) inputs, and 01 (one) output, all independent of each other.
The input variable “vibration analysis”
For the determination of each variable, it was convenient to divide
them into strips to approximate the actual situation to be checked. The
calculation of these ranges on a scale according to Tables 13.6 13.12 is
shown next.
As the first level of variation “vibration level,” let us consider that
better variable levels were subdivided into four variables, normal, permis-
sive, alert, and critical, each corresponding to the classification of vibra-
tion, velocity, and displacement levels measured in the equipment.
The input variable lubricating oil
The “level of analysis of the lubricating oil” can be presented, for
example, with the water content in the oil, solid, and nonlubricated particle
content (iron and obre), the energy sources of the dispatch of load for gen-
eration of energy. The levels of analysis of the command type were subdi-
vided into three variables, correspondence and information quality [9].