Page 51 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 51
26 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
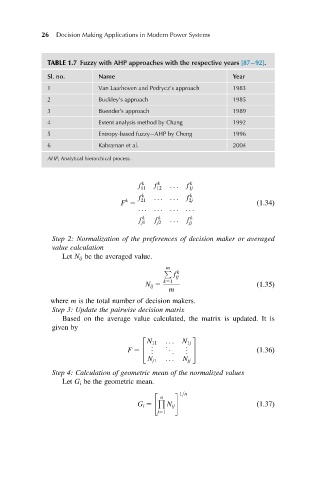
TABLE 1.7 Fuzzy with AHP approaches with the respective years [87 92].
Sl. no. Name Year
1 Van Laarhoven and Pedrycz’s approach 1983
2 Buckley’s approach 1985
3 Boender’s approach 1989
4 Extent analysis method by Chang 1992
5 Entropy-based fuzzy AHP by Cheng 1996
6 Kahraman et al. 2004
AHP, Analytical hierarchical process.
f k f k ... f k
11 12 1j
f k ... ... f k
k
F 5 21 2j ð1:34Þ
... ... ... ...
f k f k ... f k
j1 j2 jj
Step 2: Normalization of the preferences of decision maker or averaged
value calculation
Let N ij be the averaged value.
m
f
P k
ij
N ij 5 k51 ð1:35Þ
m
where m is the total number of decision makers.
Step 3: Update the pairwise decision matrix
Based on the average value calculated, the matrix is updated. It is
given by
2 ... 3
N 11 N 1j
F 5 4 ^ & ^ 5 ð1:36Þ
...
N j1 N jj
Step 4: Calculation of geometric mean of the normalized values
Let G i be the geometric mean.
" # 1=n
n
G i 5 L N ij ð1:37Þ
j51