Page 55 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 55
30 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
1 WN ij WN j
L
ij
0 x
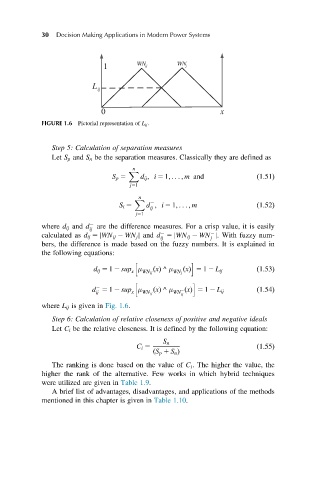
FIGURE 1.6 Pictorial representation of L ij :
Step 5: Calculation of separation measures
Let S p and S n be the separation measures. Classically they are defined as
n
X
S p 5 d ij ; i 5 1; ... ; m and ð1:51Þ
j51
n
X 2
S i 5 d ; i 5 1; ... ; m ð1:52Þ
ij
j51
where d ij and d 2 are the difference measures. For a crisp value, it is easily
ij
2
2
calculated as d ij 5 jWN ij 2 WN j j and d 5 jWN ij 2 WN j. With fuzzy num-
j
ij
bers, the difference is made based on the fuzzy numbers. It is explained in
the following equations:
h i
d ij 5 1 2 sup μ x ðÞ ^ μ
x WN ij WN j x ðÞ 5 1 2 L ij ð1:53Þ
h i
d 5 1 2 sup μ x ðÞ ^ μ
2
ij x WN ij WN 2 xðÞ 5 1 2 L ij ð1:54Þ
ij
where L ij is given in Fig. 1.6.
Step 6: Calculation of relative closeness of positive and negative ideals
Let C i be the relative closeness. It is defined by the following equation:
S n
C i 5 ð1:55Þ
ðS p 1 S n Þ
The ranking is done based on the value of C i . The higher the value, the
higher the rank of the alternative. Few works in which hybrid techniques
were utilized are given in Table 1.9.
A brief list of advantages, disadvantages, and applications of the methods
mentioned in this chapter is given in Table 1.10.