Page 413 - Design and Operation of Heat Exchangers and their Networks
P. 413
396 Design and operation of heat exchangers and their networks
the fluids and solid material can be omitted, and the thermal capacity of
the solid wall does not need to be considered. The measured data during
a certain time interval will be averaged, which can smooth the signal
fluctuations.
8.2.1 Test under constant heat flux
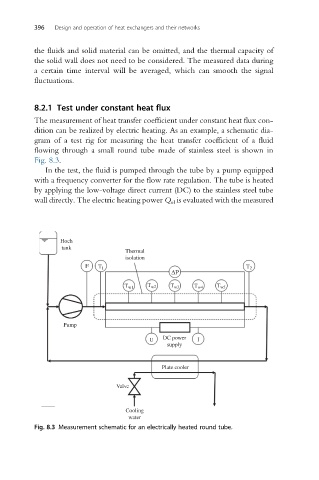
The measurement of heat transfer coefficient under constant heat flux con-
dition can be realized by electric heating. As an example, a schematic dia-
gram of a test rig for measuring the heat transfer coefficient of a fluid
flowing through a small round tube made of stainless steel is shown in
Fig. 8.3.
In the test, the fluid is pumped through the tube by a pump equipped
with a frequency converter for the flow rate regulation. The tube is heated
by applying the low-voltage direct current (DC) to the stainless steel tube
wall directly. The electric heating power Q el is evaluated with the measured
Hoch
tank
Thermal
isolation
F T 1 T 2
ΔP
T w1 T w2 T w3 T w4 T w5
Pump
DC power
U I
supply
Plate cooler
Valve
Cooling
water
Fig. 8.3 Measurement schematic for an electrically heated round tube.