Page 187 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 187
166 Cha pte r Ni ne
of environmental performance quite challenging. While product
development teams need not analyze each life-cycle stage in exhaus-
tive detail, they need to be aware of those environmental issues, at
any stage of the life cycle, that are relevant to either customer needs
or technical and financial constraints.
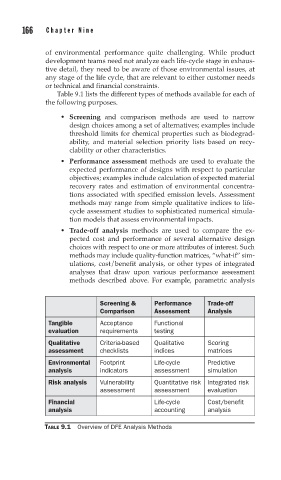
Table 9.1 lists the different types of methods available for each of
the following purposes.
• Screening and comparison methods are used to narrow
design choices among a set of alternatives; examples include
threshold limits for chemical properties such as biodegrad-
ability, and material selection priority lists based on recy-
clability or other characteristics.
• Performance assessment methods are used to evaluate the
expected performance of designs with respect to particular
objectives; examples include calculation of expected material
recovery rates and estimation of environmental concentra-
tions associated with specified emission levels. Assessment
methods may range from simple qualitative indices to life-
cycle assessment studies to sophisticated numerical simula-
tion models that assess environmental impacts.
• Trade-off analysis methods are used to compare the ex -
pected cost and performance of several alternative design
choices with respect to one or more attributes of interest. Such
methods may include quality-function matrices, “what-if” sim-
ulations, cost/benefit analysis, or other types of integrated
analyses that draw upon various performance assessment
methods described above. For example, parametric analysis
Screening & Performance Trade-off
Comparison Assessment Analysis
Tangible Acceptance Functional
evaluation requirements testing
Qualitative Criteria-based Qualitative Scoring
assessment checklists indices matrices
Environmental Footprint Life-cycle Predictive
analysis indicators assessment simulation
Risk analysis Vulnerability Quantitative risk Integrated risk
assessment assessment evaluation
Financial Life-cycle Cost/benefit
analysis accounting analysis
TABLE 9.1 Overview of DFE Analysis Methods