Page 181 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 181
154 Chapter Five
value proposition to the customer. The collection of all design matrices
obtained up to the detailing level that is satisfactory to the team forms
the structure. The structure provides a means to track the chain of
effects for design changes as they propagate across the design. The
zigzagging process starts by using the minimum set of functional
requirements that deliver the design tasks as defined by the customer
and obtained from phase 2 QFD. The zigzagging process is guided by
the creative and heuristic process of functional requirements definition
through logical questions offered by the zigzagging method (Chap. 8).
This structural definition is judged by following design axioms:
Axiom 1: The Independence Axiom Maintain the independence of the
functional requirements.
Axiom 2: The Information Axiom Minimize the information content in a
design.
After satisfying the independence axiom, design simplicity is pur-
sued by minimizing the information contents per axiom 2. In this con-
text, information content is defined as a measure of complexity and is
related to the probability of successfully manufacturing (producing)
the design as intended. Because of ignorance and other inhibitors, the
exact deployment of design axiom might be concurrently infeasible as
a result of technological and cost limitations. Under these circum-
stances, different degrees of conceptual vulnerabilities are established
in the measures (criteria) related to the unsatisfied axiom. For exam-
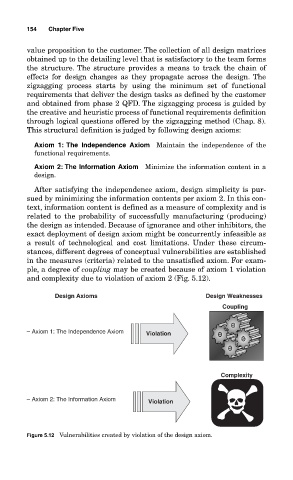
ple, a degree of coupling may be created because of axiom 1 violation
and complexity due to violation of axiom 2 (Fig. 5.12).
Design Axioms Design Weaknesses
Coupling
– Axiom 1: The Independence Axiom Violation
Complexity
– Axiom 2: The Information Axiom Violation
Figure 5.12 Vulnerabilities created by violation of the design axiom.