Page 185 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 185
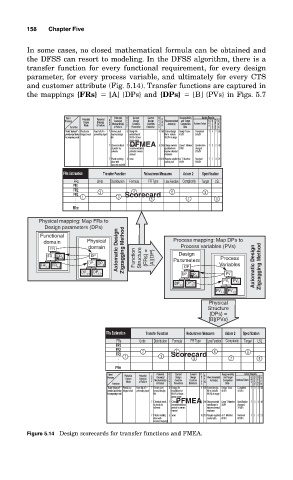
158 Chapter Five
In some cases, no closed mathematical formula can be obtained and
the DFSS can resort to modeling. In the DFSS algorithm, there is a
transfer function for every functional requirement, for every design
parameter, for every process variable, and ultimately for every CTS
and customer attribute (Fig. 5.14). Transfer functions are captured in
the mappings {FRs} [A] {DPs} and {DPs} [B] {PVs} in Figs. 5.7
Item / Potential O Current Current D Responsibility Action Results
Process Potential Potential S Cause(s)/ c Design Design e R. P. Recommended and Target S O D R.
Failure Effect(s) e c Controls Controls t Action(s) Completion Actions Taken e c e
Mode of Failure v Mechanism(s) u e N. v c t P.
Function of Failure r Prevention Detection c Date u e N.
r c
Thumb "keyboard" — Plastic key Keys fall off — 7 Device used 6 Design life 4 168 Extend design Design Team: Completed 7 4 2 56
provides input device hinges break preventing input beyond design established at life to include 4/1/01 5/15/01
for composing e-mail life 99.5% of focus 99.9% of usage
group usage
7 Chemical attack 7 Cleaning DFMEA 5 245 Change material Casey T. Member: Specification 7 3 2 42
of plastic by recommendations specification to 3/1/01 changed:
solvents printed in owners improve chemical 2/15/01
manual resistance
7 Plastic molding 3 none 10 210 Require supplier'sJo T. Member: Received 7 1 3 21
done with control plan 6/1/01 6/15/01
incorrect material
FRs Estimation Transfer Function Robustness Measures Axiom 2 Specification
FRs Units Distribution Formula FR Type Loss Function Complexity Target LSL
FR1
FR2 2 4 4 6 6 8 8
FR3 1 33 Scorecard
: 5 5 7 7 9 9
:
FRm
Physical mapping: Map FRs to
Design parameters (DPs)
Functional
domain Physical Process mapping: Map DPs to
FR domain Axiomatic Design Zigzagging Method Process variables (PVs)
DP Design
FR 1 FR 2 Function Structure {FRs} = [A]{DP} Parameters Process
DP 1 DP 2 Variables
FR 1.1 FR 1.2 DP Axiomatic Design Zigzagging Method
DP 1.1 DP 1.2 PV
DP 1 DP 2
PV 1 PV 2
DP 1.1 DP 1.2
PV 1.1 PV 1.2
Physical
Structure
{DPs} =
[B]{PVs}
FRs Estimation Transfer Function Robustness Measures Axiom 2 Specification
FRs Units Distribution Formula FR Type Loss Function Complexity Target LSL
FR1
FR2 2 4 4 6 6 8 8
FR3 1 33 Scorecard
: 5 5 7 7 9 9
:
FRm
Item / Potential O Current Current D Responsibility Action Results
Process Potential Potential S Cause(s)/ c Design Design e R. P. Recommended and Target S O D R.
Failure Effect(s) e c Controls Controls t Action(s) Completion Actions Taken e c e P.
Mode of Failure v Mechanism(s) u e N. v c t
Function of Failure r Prevention Detection c Date u e N.
r c
Thumb "keyboard" — Plastic key Keys fall off — 7 Device used 6 Design life 4 168 Extend design Design Team: Completed 7 4 2 56
provides input device hinges break preventing input beyond design established at life to include 4/1/01 5/15/01
for composing e-mail life 99.5% of focus 99.9% of usage
group usage
7 Chemical attack 7 Cleaning PFMEA 5 245 Change material Casey T. Member: Specification 7 3 2 42
of plastic by recommendations specification to 3/1/01 changed:
solvents printed in owners improve chemical 2/15/01
manual resistance
7 Plastic molding 3 none 10 210 Require supplier'sJo T. Member: Received 7 1 3 21
done with control plan 6/1/01 6/15/01
incorrect material
Figure 5.14 Design scorecards for transfer functions and FMEA.