Page 389 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 389
Design for X 359
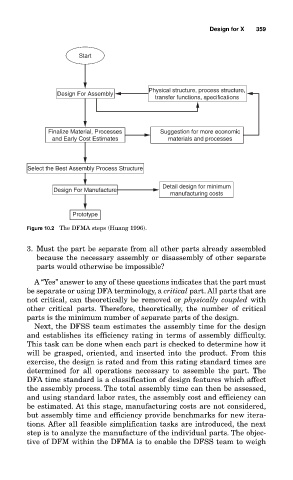
Start
Physical structure, process structure,
Design For Assembly
transfer functions, specifications
Finalize Material, Processes Suggestion for more economic
and Early Cost Estimates materials and processes
Select the Best Assembly Process Structure
Detail design for minimum
Design For Manufacture
manufacturing costs
Prototype
Figure 10.2 The DFMA steps (Huang 1996).
3. Must the part be separate from all other parts already assembled
because the necessary assembly or disassembly of other separate
parts would otherwise be impossible?
A “Yes” answer to any of these questions indicates that the part must
be separate or using DFA terminology, a critical part. All parts that are
not critical, can theoretically be removed or physically coupled with
other critical parts. Therefore, theoretically, the number of critical
parts is the minimum number of separate parts of the design.
Next, the DFSS team estimates the assembly time for the design
and establishes its efficiency rating in terms of assembly difficulty.
This task can be done when each part is checked to determine how it
will be grasped, oriented, and inserted into the product. From this
exercise, the design is rated and from this rating standard times are
determined for all operations necessary to assemble the part. The
DFA time standard is a classification of design features which affect
the assembly process. The total assembly time can then be assessed,
and using standard labor rates, the assembly cost and efficiency can
be estimated. At this stage, manufacturing costs are not considered,
but assembly time and efficiency provide benchmarks for new itera-
tions. After all feasible simplification tasks are introduced, the next
step is to analyze the manufacture of the individual parts. The objec-
tive of DFM within the DFMA is to enable the DFSS team to weigh