Page 418 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 418
Design for X 385
Loss Profit
A
A
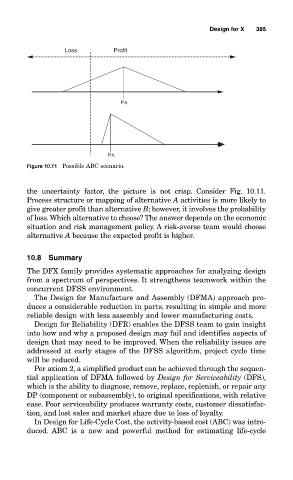
Figure 10.11 Possible ABC scenario.
the uncertainty factor, the picture is not crisp. Consider Fig. 10.11.
Process structure or mapping of alternative A activities is more likely to
give greater profit than alternative B; however, it involves the probability
of loss.Which alternative to choose? The answer depends on the economic
situation and risk management policy. A risk-averse team would choose
alternative A because the expected profit is higher.
10.8 Summary
The DFX family provides systematic approaches for analyzing design
from a spectrum of perspectives. It strengthens teamwork within the
concurrent DFSS environment.
The Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DFMA) approach pro-
duces a considerable reduction in parts, resulting in simple and more
reliable design with less assembly and lower manufacturing costs.
Design for Reliability (DFR) enables the DFSS team to gain insight
into how and why a proposed design may fail and identifies aspects of
design that may need to be improved. When the reliability issues are
addressed at early stages of the DFSS algorithm, project cycle time
will be reduced.
Per axiom 2, a simplified product can be achieved through the sequen-
tial application of DFMA followed by Design for Serviceability (DFS),
which is the ability to diagnose, remove, replace, replenish, or repair any
DP (component or subassembly), to original specifications, with relative
ease. Poor serviceability produces warranty costs, customer dissatisfac-
tion, and lost sales and market share due to loss of loyalty.
In Design for Life-Cycle Cost, the activity-based cost (ABC) was intro-
duced. ABC is a new and powerful method for estimating life-cycle