Page 433 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 433
Failure Mode–Effect Analysis 397
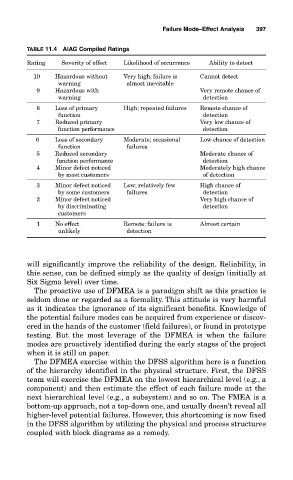
TABLE 11.4 AIAG Compiled Ratings
Rating Severity of effect Likelihood of occurrence Ability to detect
10 Hazardous without Very high; failure is Cannot detect
warning almost inevitable
9 Hazardous with Very remote chance of
warning detection
8 Loss of primary High; repeated failures Remote chance of
function detection
7 Reduced primary Very low chance of
function performance detection
6 Loss of secondary Moderate; occasional Low chance of detection
function failures
5 Reduced secondary Moderate chance of
function performance detection
4 Minor defect noticed Moderately high chance
by most customers of detection
3 Minor defect noticed Low; relatively few High chance of
by some customers failures detection
2 Minor defect noticed Very high chance of
by discriminating detection
customers
1 No effect Remote: failure is Almost certain
unlikely detection
will significantly improve the reliability of the design. Reliability, in
this sense, can be defined simply as the quality of design (initially at
Six Sigma level) over time.
The proactive use of DFMEA is a paradigm shift as this practice is
seldom done or regarded as a formality. This attitude is very harmful
as it indicates the ignorance of its significant benefits. Knowledge of
the potential failure modes can be acquired from experience or discov-
ered in the hands of the customer (field failures), or found in prototype
testing. But the most leverage of the DFMEA is when the failure
modes are proactively identified during the early stages of the project
when it is still on paper.
The DFMEA exercise within the DFSS algorithm here is a function
of the hierarchy identified in the physical structure. First, the DFSS
team will exercise the DFMEA on the lowest hierarchical level (e.g., a
component) and then estimate the effect of each failure mode at the
next hierarchical level (e.g., a subsystem) and so on. The FMEA is a
bottom-up approach, not a top-down one, and usually doesn’t reveal all
higher-level potential failures. However, this shortcoming is now fixed
in the DFSS algorithm by utilizing the physical and process structures
coupled with block diagrams as a remedy.