Page 47 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 47
Six Sigma and Lean Fundamentals 25
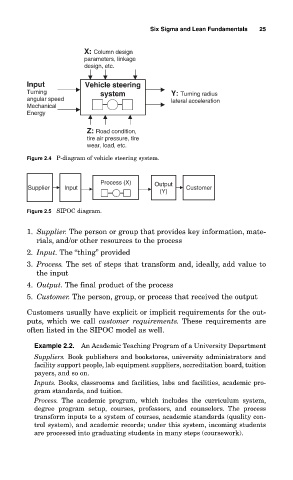
X: Column design
parameters, linkage
design, etc.
Input Vehicle steering
Turning system Y: Turning radius
angular speed lateral acceleration
Mechanical
Energy
Z: Road condition,
tire air pressure, tire
wear, load, etc.
Figure 2.4 P-diagram of vehicle steering system.
Process (X) Output
Supplier Input Customer
(Y)
Figure 2.5 SIPOC diagram.
1. Supplier. The person or group that provides key information, mate-
rials, and/or other resources to the process
2. Input. The “thing” provided
3. Process. The set of steps that transform and, ideally, add value to
the input
4. Output. The final product of the process
5. Customer. The person, group, or process that received the output
Customers usually have explicit or implicit requirements for the out-
puts, which we call customer requirements. These requirements are
often listed in the SIPOC model as well.
Example 2.2. An Academic Teaching Program of a University Department
Suppliers. Book publishers and bookstores, university administrators and
facility support people, lab equipment suppliers, accreditation board, tuition
payers, and so on.
Inputs. Books, classrooms and facilities, labs and facilities, academic pro-
gram standards, and tuition.
Process. The academic program, which includes the curriculum system,
degree program setup, courses, professors, and counselors. The process
transform inputs to a system of courses, academic standards (quality con-
trol system), and academic records; under this system, incoming students
are processed into graduating students in many steps (coursework).