Page 54 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 54
32 Chapter Two
developed in the late 1980s and takes into account the proximity of the
process mean to the ideal performance target T.
USL LSL
C pm
6 ( T ) 2
2
When the process mean is centered between the specification limits
and the process mean is on the target T, then C p C pk C pm . When a
process mean departs from the target value T, there is a substantive
effect on the capability index. In the C pk example above, if the target
value were T 21, C pm would be calculated as
24 18
C pm 1.281
6 0.8 (22 21) 2
2
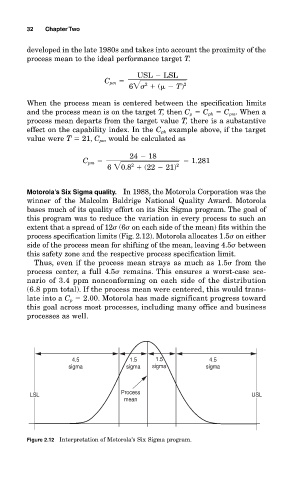
Motorola’s Six Sigma quality. In 1988, the Motorola Corporation was the
winner of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. Motorola
bases much of its quality effort on its Six Sigma program. The goal of
this program was to reduce the variation in every process to such an
extent that a spread of 12 (6 on each side of the mean) fits within the
process specification limits (Fig. 2.12). Motorola allocates 1.5 on either
side of the process mean for shifting of the mean, leaving 4.5 between
this safety zone and the respective process specification limit.
Thus, even if the process mean strays as much as 1.5 from the
process center, a full 4.5 remains. This ensures a worst-case sce-
nario of 3.4 ppm nonconforming on each side of the distribution
(6.8 ppm total). If the process mean were centered, this would trans-
late into a C p 2.00. Motorola has made significant progress toward
this goal across most processes, including many office and business
processes as well.
4.5 1.5 1.5 4.5
sigma sigma sigma sigma
Process
LSL USL
mean
Figure 2.12 Interpretation of Motorola’s Six Sigma program.