Page 340 - Design for Six Sigma for Service (Six SIGMA Operational Methods)
P. 340
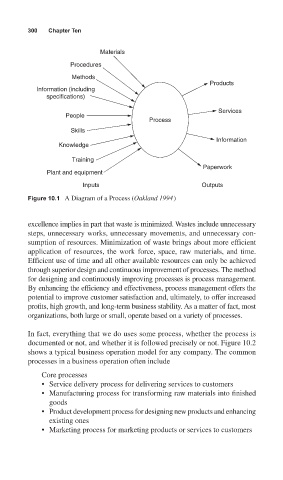
300 Chapter Ten
Materials
Procedures
Methods
Products
Information (including
specifications)
Services
People
Process
Skills
Information
Knowledge
Training
Paperwork
Plant and equipment
Inputs Outputs
Figure 10.1 A Diagram of a Process (Oakland 1994)
excellence implies in part that waste is minimized. Wastes include unnecessary
steps, unnecessary works, unnecessary movements, and unnecessary con-
sumption of resources. Minimization of waste brings about more efficient
application of resources, the work force, space, raw materials, and time.
Efficient use of time and all other available resources can only be achieved
through superior design and continuous improvement of processes. The method
for designing and continuously improving processes is process management.
By enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness, process management offers the
potential to improve customer satisfaction and, ultimately, to offer increased
profits, high growth, and long-term business stability. As a matter of fact, most
organizations, both large or small, operate based on a variety of processes.
In fact, everything that we do uses some process, whether the process is
documented or not, and whether it is followed precisely or not. Figure 10.2
shows a typical business operation model for any company. The common
processes in a business operation often include
Core processes
• Service delivery process for delivering services to customers
• Manufacturing process for transforming raw materials into finished
goods
• Product development process for designing new products and enhancing
existing ones
• Marketing process for marketing products or services to customers