Page 99 - Design for Six Sigma for Service (Six SIGMA Operational Methods)
P. 99
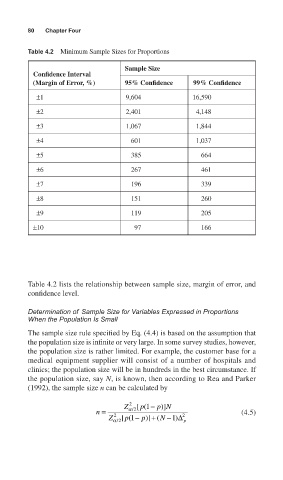
80 Chapter Four
Table 4.2 Minimum Sample Sizes for Proportions
Sample Size
Confidence Interval
(Margin of Error, %) 95% Confidence 99% Confidence
±1 9,604 16,590
±2 2,401 4,148
±3 1,067 1,844
±4 601 1,037
±5 385 664
±6 267 461
±7 196 339
±8 151 260
±9 119 205
±10 97 166
Table 4.2 lists the relationship between sample size, margin of error, and
confidence level.
Determination of Sample Size for Variables Expressed in Proportions
When the Population Is Small
The sample size rule specified by Eq. (4.4) is based on the assumption that
the population size is infinite or very large. In some survey studies, however,
the population size is rather limited. For example, the customer base for a
medical equipment supplier will consist of a number of hospitals and
clinics; the population size will be in hundreds in the best circumstance. If
the population size, say N, is known, then according to Rea and Parker
(1992), the sample size n can be calculated by
p − )]1
Z 2 [( p N
n = a/2 (4.5)
p − )] (1
Z 2 [( p + N − )1 ∆ 2
a/2 p