Page 115 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 115
MATERIALS OF MASONRY CONSTRUCTION 3.9
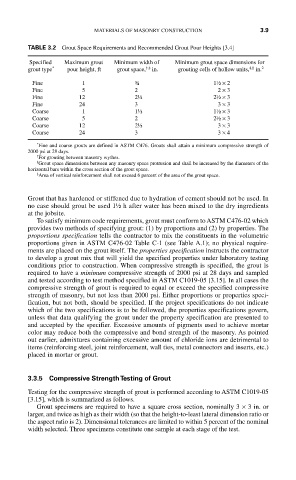
TABLE 3.2 Grout Space Requirements and Recommended Grout Pour Heights [3.4]
Specified Maximum grout Minimum width of Minimum grout space dimensions for
‡,§
†,‡
*
grout type pour height, ft grout space, in. grouting cells of hollow units, in. 2
Fine 1 ¾ 1½ × 2
Fine 5 2 2 × 3
Fine 12 2½ 2½ × 3
Fine 24 3 3 × 3
Coarse 1 1½ 1½ × 3
Coarse 5 2 2½ × 3
Coarse 12 2½ 3 × 3
Coarse 24 3 3 × 4
*
Fine and coarse grouts are defined in ASTM C476. Grouts shall attain a minimum compressive strength of
2000 psi at 28 days.
†
For grouting between masonry wythes.
‡
Grout space dimensions between any masonry space protrusion and shall be increased by the diameters of the
horizontal bars within the cross section of the grout space.
§
Area of vertical reinforcement shall not exceed 6 percent of the area of the grout space.
Grout that has hardened or stiffened due to hydration of cement should not be used. In
no case should grout be used 1½ h after water has been mixed to the dry ingredients
at the jobsite.
To satisfy minimum code requirements, grout must conform to ASTM C476-02 which
provides two methods of specifying grout: (1) by proportions and (2) by properties. The
proportions specification tells the contractor to mix the constituents in the volumetric
proportions given in ASTM C476-02 Table C-1 (see Table A.1); no physical require-
ments are placed on the grout itself. The properties specification instructs the contractor
to develop a grout mix that will yield the specified properties under laboratory testing
conditions prior to construction. When compressive strength is specified, the grout is
required to have a minimum compressive strength of 2000 psi at 28 days and sampled
and tested according to test method specified in ASTM C1019-05 [3.15]. In all cases the
compressive strength of grout is required to equal or exceed the specified compressive
strength of masonry, but not less than 2000 psi. Either proportions or properties speci-
fication, but not both, should be specified. If the project specifications do not indicate
which of the two specifications is to be followed, the properties specifications govern,
unless that data qualifying the grout under the property specification are presented to
and accepted by the specifier. Excessive amounts of pigments used to achieve mortar
color may reduce both the compressive and bond strength of the masonry. As pointed
out earlier, admixtures containing excessive amount of chloride ions are detrimental to
items (reinforcing steel, joint reinforcement, wall ties, metal connectors and inserts, etc.)
placed in mortar or grout.
3.3.5 Compressive Strength Testing of Grout
Testing for the compressive strength of grout is performed according to ASTM C1019-05
[3.15], which is summarized as follows.
Grout specimens are required to have a square cross section, nominally 3 × 3 in. or
larger, and twice as high as their width (so that the height-to-least lateral dimension ratio or
the aspect ratio is 2). Dimensional tolerances are limited to within 5 percent of the nominal
width selected. Three specimens constitute one sample at each stage of the test.