Page 182 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 182
5.5 Intensification of Process Functions 167
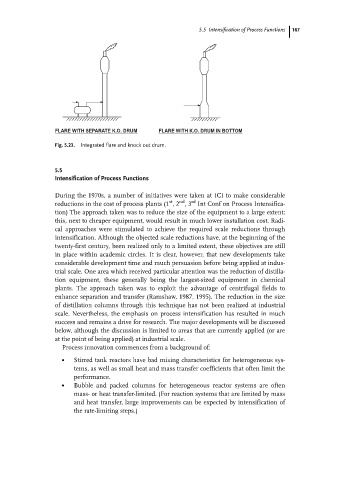
FLARE WITH SEPARATE K.O. DRUM FLARE WITH K.O. DRUM IN BOTTOM
Fig. 5.23. Integrated flare and knock out drum.
5.5
Intensification of Process Functions
During the 1970s, a number of initiatives were taken at ICI to make considerable
nd
st
rd
reductions in the cost of process plants (1 ,2 ,3 Int Conf on Process Intensifica-
tion) The approach taken was to reduce the size of the equipment to a large extent;
this, next to cheaper equipment, would result in much lower installation cost. Radi-
cal approaches were stimulated to achieve the required scale reductions through
intensification. Although the objected scale reductions have, at the beginning of the
twenty-first century, been realized only to a limited extent, these objectives are still
in place within academic circles. It is clear, however, that new developments take
considerable development time and much persuasion before being applied at indus-
trial scale. One area which received particular attention was the reduction of distilla-
tion equipment, these generally being the largest-sized equipment in chemical
plants. The approach taken was to exploit the advantage of centrifugal fields to
enhance separation and transfer (Ramshaw, 1987, 1995). The reduction in the size
of distillation columns through this technique has not been realized at industrial
scale. Nevertheless, the emphasis on process intensification has resulted in much
success and remains a drive for research. The major developments will be discussed
below, although the discussion is limited to areas that are currently applied (or are
at the point of being applied) at industrial scale.
Process innovation commences from a background of:
. Stirred tank reactors have bad mixing characteristics for heterogeneous sys-
tems, as well as small heat and mass transfer coefficients that often limit the
performance.
. Bubble and packed columns for heterogeneous reactor systems are often
mass- or heat transfer-limited. (For reaction systems that are limited by mass
and heat transfer, large improvements can be expected by intensification of
the rate-limiting steps.)