Page 246 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 246
232 Chapter 6 Process Design Based on Reliability
The different mathematical techniques for distribution analysis and the determina-
tion of the confidence are discussed in the referred text books. The selection of dis-
tribution models and its parameters is supported by commercial software packages,
such as SPAR (Clockwork Design Inc.).
6.2.4
Reliability Modeling
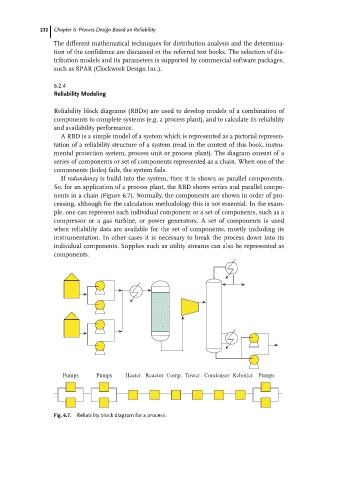
Reliability block diagrams (RBDs) are used to develop models of a combination of
components to complete systems (e.g. a process plant), and to calculate its reliability
and availability performance.
A RBD is a simple model of a system which is represented as a pictorial represen-
tation of a reliability structure of a system (read in the context of this book, instru-
mental protection system, process unit or process plant). The diagram consist of a
series of components or set of components represented as a chain. When one of the
components (links) fails, the system fails.
If redundancy is build into the system, then it is shown as parallel components.
So, for an application of a process plant, the RBD shows series and parallel compo-
nents in a chain (Figure 6.7). Normally, the components are shown in order of pro-
cessing, although for the calculation methodology this is not essential. In the exam-
ple, one can represent each individual component or a set of components, such as a
compressor or a gas turbine, or power generators. A set of components is used
when reliability data are available for the set of components, mostly including its
instrumentation. In other cases it is necessary to break the process down into its
individual components. Supplies such as utility streams can also be represented as
components.
Pumps Pumps Heater Reactor Comp. Tower Condensor Reboiler Pumps
Fig. 6.7. Reliability block diagram for a process.