Page 206 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 206
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:16
Expressive Vocalization System 187
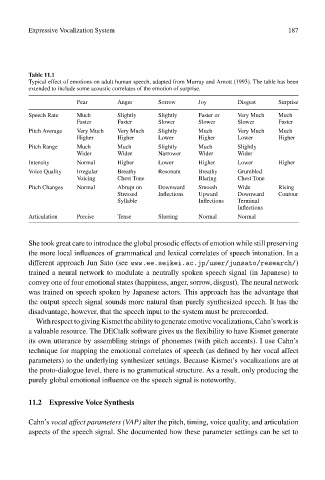
Table 11.1
Typical effect of emotions on adult human speech, adapted from Murray and Arnott (1993). The table has been
extended to include some acoustic correlates of the emotion of surprise.
Fear Anger Sorrow Joy Disgust Surprise
Speech Rate Much Slightly Slightly Faster or Very Much Much
Faster Faster Slower Slower Slower Faster
Pitch Average Very Much Very Much Slightly Much Very Much Much
Higher Higher Lower Higher Lower Higher
Pitch Range Much Much Slightly Much Slightly
Wider Wider Narrower Wider Wider
Intensity Normal Higher Lower Higher Lower Higher
Voice Quality Irregular Breathy Resonant Breathy Grumbled
Voicing Chest Tone Blaring Chest Tone
Pitch Changes Normal Abrupt on Downward Smooth Wide Rising
Stressed Inflections Upward Downward Contour
Syllable Inflections Terminal
Inflections
Articulation Precise Tense Slurring Normal Normal
She took great care to introduce the global prosodic effects of emotion while still preserving
the more local influences of grammatical and lexical correlates of speech intonation. In a
different approach Jun Sato (see www.ee.seikei.ac.jp/user/junsato/research/)
trained a neural network to modulate a neutrally spoken speech signal (in Japanese) to
convey one of four emotional states (happiness, anger, sorrow, disgust). The neural network
was trained on speech spoken by Japanese actors. This approach has the advantage that
the output speech signal sounds more natural than purely synthesized speech. It has the
disadvantage, however, that the speech input to the system must be prerecorded.
WithrespecttogivingKismettheabilitytogenerateemotivevocalizations,Cahn’sworkis
a valuable resource. The DECtalk software gives us the flexibility to have Kismet generate
its own utterance by assembling strings of phonemes (with pitch accents). I use Cahn’s
technique for mapping the emotional correlates of speech (as defined by her vocal affect
parameters) to the underlying synthesizer settings. Because Kismet’s vocalizations are at
the proto-dialogue level, there is no grammatical structure. As a result, only producing the
purely global emotional influence on the speech signal is noteworthy.
11.2 Expressive Voice Synthesis
Cahn’s vocal affect parameters (VAP) alter the pitch, timing, voice quality, and articulation
aspects of the speech signal. She documented how these parameter settings can be set to