Page 96 - Designing Sociable Robots
P. 96
breazeal-79017 book March 18, 2002 14:2
The Vision System 77
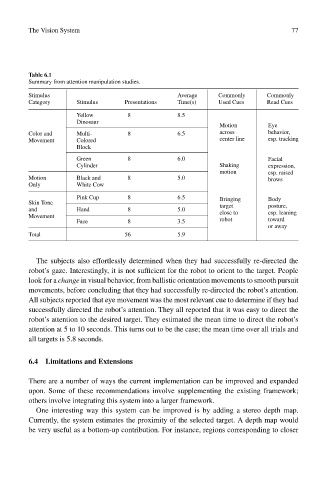
Table 6.1
Summary from attention manipulation studies.
Stimulus Average Commonly Commonly
Category Stimulus Presentations Time(s) Used Cues Read Cues
Yellow 8 8.5
Dinosaur
Motion Eye
Color and Multi- 8 6.5 across behavior,
Movement Colored center line esp. tracking
Block
Green 8 6.0 Facial
Cylinder Shaking expression,
motion esp. raised
Motion Black and 8 5.0 brows
Only White Cow
Pink Cup 8 6.5 Bringing Body
Skin Tone
and Hand 8 5.0 target posture,
Movement close to esp. leaning
Face 8 3.5 robot toward
or away
Total 56 5.9
The subjects also effortlessly determined when they had successfully re-directed the
robot’s gaze. Interestingly, it is not sufficient for the robot to orient to the target. People
look for a change in visual behavior, from ballistic orientation movements to smooth pursuit
movements, before concluding that they had successfully re-directed the robot’s attention.
All subjects reported that eye movement was the most relevant cue to determine if they had
successfully directed the robot’s attention. They all reported that it was easy to direct the
robot’s attention to the desired target. They estimated the mean time to direct the robot’s
attention at 5 to 10 seconds. This turns out to be the case; the mean time over all trials and
all targets is 5.8 seconds.
6.4 Limitations and Extensions
There are a number of ways the current implementation can be improved and expanded
upon. Some of these recommendations involve supplementing the existing framework;
others involve integrating this system into a larger framework.
One interesting way this system can be improved is by adding a stereo depth map.
Currently, the system estimates the proximity of the selected target. A depth map would
be very useful as a bottom-up contribution. For instance, regions corresponding to closer