Page 182 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 182
Image Geometric Rectification 147
Calculation of this distortion requires measurement of the radial dis-
tance r from the principal point of the photograph [Eq. (5.3)]. The
distortion on the photography Δr is calculated as
Δ= Hr 3 (5.3)
r
2 Rf 2
where f is focal length of the camera used to take the photograph, and
H and R are as defined previously.
5.1.2 Sensor Distortions
Off-Nadir Scale Distortion
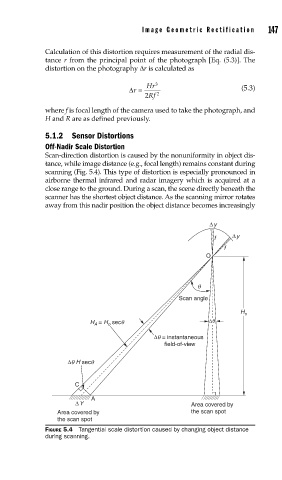
Scan-direction distortion is caused by the nonuniformity in object dis-
tance, while image distance (e.g., focal length) remains constant during
scanning (Fig. 5.4). This type of distortion is especially pronounced in
airborne thermal infrared and radar imagery which is acquired at a
close range to the ground. During a scan, the scene directly beneath the
scanner has the shortest object distance. As the scanning mirror rotates
away from this nadir position the object distance becomes increasingly
Δy
f Δy
f
O
q
Scan angle
H o
o
A
H = H secq Δq
Δq = instantaneous
field-of-view
Δq H secq
C
A
ΔY Area covered by
Area covered by the scan spot
the scan spot
FIGURE 5.4 Tangential scale distortion caused by changing object distance
during scanning.