Page 36 - Discrimination at Work The Psychological and Organizational Bases
P. 36
12
DOVIDIO AND HEBL
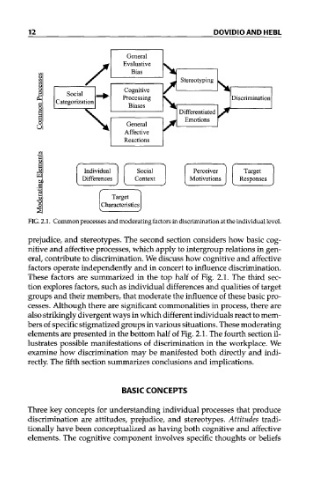
FIG. 2.1. Common processes and moderating factors in discrimination at the individual level.
prejudice, and stereotypes. The second section considers how basic cog
nitive and affective processes, which apply to intergroup relations in gen
eral, contribute to discrimination. We discuss how cognitive and affective
factors operate independently and in concert to influence discrimination.
These factors are summarized in the top half of Fig. 2.1. The third sec
tion explores factors, such as individual differences and qualities of target
groups and their members, that moderate the influence of these basic pro
cesses. Although there are significant commonalities in process, there are
also strikingly divergent ways in which different individuals react to mem
bers of specific stigmatized groups in various situations. These moderating
elements are presented in the bottom half of Fig. 2.1. The fourth section il
lustrates possible manifestations of discrimination in the workplace. We
examine how discrimination may be manifested both directly and indi
rectly. The fifth section summarizes conclusions and implications.
BASIC CONCEPTS
Three key concepts for understanding individual processes that produce
discrimination are attitudes, prejudice, and stereotypes. Attitudes tradi
tionally have been conceptualized as having both cognitive and affective
elements. The cognitive component involves specific thoughts or beliefs