Page 112 - Distillation theory
P. 112
P1: FCH/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521832772c04 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 17:49
86 Trajectories of Thermodynamically Reversible Distillation
and azeotrope (points 1, 3, and 13) that are node points of stationarity lines bun-
dles (N rev ⇔ N rev ). True trajectories of reversible distillation, in contrast to the
fictitious ones, always start in the product point and end in the node point of the
(2) (2)
bundle (point of the component or azeotrope) Reg ⇒ N rev or Reg ⇒ N rev or
D B
at the same boundary element of the concentration simplex where the product
(2) (2) (2) (2)
point is located Reg ⇔ Reg or Reg ⇔ Reg . In the last case, the trajectory
D D B B
bundle does not have node points (bundle in Fig. 4.7a to the left of line α 23 can
serve as an example of such bundle).
Therefore, the concentration simplex can contain one or several regions of
reversible distillation Reg h rev,r or Reg l rev,s for each section.
The region of reversible distillation can contain one or several reversible distil-
lation trajectory bundles (lines of stationarity). Some of these bundles can be true;
some of them can be fictitious. Fictitious bundles always have two node points and
true ones have one node point or no node point.
4.3.2. Condition in Tear-Off Points of the Reversible Distillation Trajectories
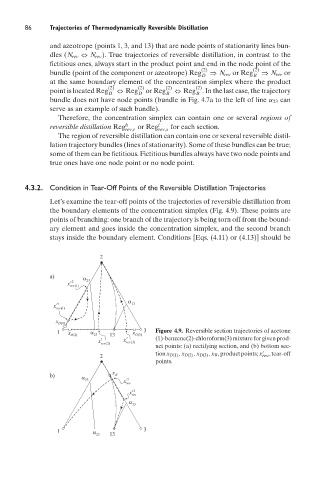
Let’s examine the tear-off points of the trajectories of reversible distillation from
the boundary elements of the concentration simplex (Fig. 4.9). These points are
points of branching: one branch of the trajectory is being torn off from the bound-
ary element and goes inside the concentration simplex, and the second branch
stays inside the boundary element. Conditions [Eqs. (4.11) or (4.13)] should be
2
a) α
x rev 2 t ) 1 ( 23
α
x 1 t 13
rev ) 1 (
x D(1)
1 α 3 Figure 4.9. Reversible section trajectories of acetone
x D(2) 23 13 t x D()3
x t rev 2( ) x rev 3( ) (1)-benzene(2)-chloroform(3) mixture for given prod-
uct points: (a) rectifying section, and (b) bottom sec-
t
2 tion x D(1) , x D(2) , x D(3) , x B , product points; x rev , tear-off
points.
b) α x B
23 x 1 t
rev
x 2 t
rev
α
13
1 α 23 13 3