Page 147 - Distillation theory
P. 147
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c05 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:15
5.3 Trajectory Tear-Off Theory and Necessary Conditions 121
2
a)
x t
s
x t
r
x
B
x D x F
1 3
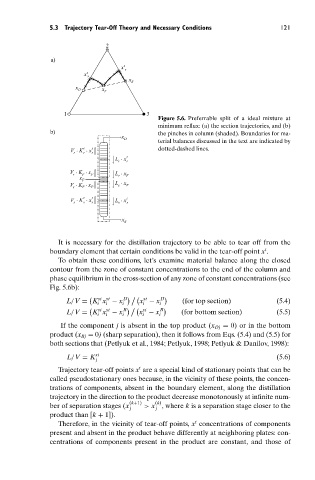
Figure 5.6. Preferrable split of a ideal mixture at
minimum reflux: (a) the section trajectories, and (b)
b) the pinches in column (shaded). Boundaries for ma-
x
D
terial balances discussed in the text are indicated by
t t dotted-dashed lines.
V . K . x
r r r
t
L . x
r r
V . K . x L . x
r F F r F
x F
V . K . x F L . x F
s
s
F
t t t
V . K . x L . x
s s s s s
x B
It is necessary for the distillation trajectory to be able to tear off from the
t
boundary element that certain conditions be valid in the tear-off point x .
To obtain these conditions, let’s examine material balance along the closed
contour from the zone of constant concentrations to the end of the column and
phase equilibrium in the cross-section of any zone of constant concentrations (see
Fig. 5.6b):
st st D st D
L/V = K x − x x − x (for top section) (5.4)
i i i i i
st st B st B
L/V = K x − x x − x (for bottom section) (5.5)
i i i i i
If the component j is absent in the top product (x Dj = 0) or in the bottom
product (x Bj = 0) (sharp separation), then it follows from Eqs. (5.4) and (5.5) for
both sections that (Petlyuk et al., 1984; Petlyuk, 1998; Petlyuk & Danilov, 1998):
L/V = K st (5.6)
j
t
Trajectory tear-off points x are a special kind of stationary points that can be
called pseudostationary ones because, in the vicinity of these points, the concen-
trations of components, absent in the boundary element, along the distillation
trajectory in the direction to the product decrease monotonously at infinite num-
(k+1) (k)
ber of separation stages (x > x , where k is a separation stage closer to the
j j
product than [k + 1]).
t
Therefore, in the vicinity of tear-off points, x concentrations of components
present and absent in the product behave differently at neighboring plates: con-
centrations of components present in the product are constant, and those of