Page 260 - Distillation theory
P. 260
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: JMT/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c07 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:18
234 Trajectories of the Finite Columns and Their Design Calculation
x D
2
x a)
F
x B
x f
x f−1
4
1
3
2
b) S 1 r
(1) (1)
x f 4 x f−1
x (2)
f−1
x (2)
f
S 1
s
1 3
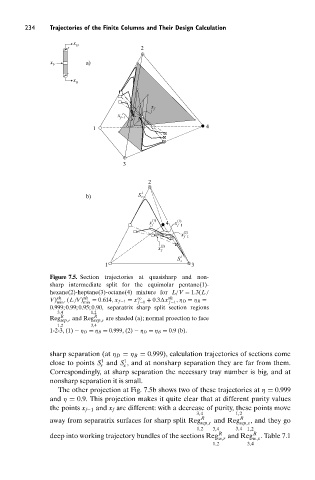
Figure 7.5. Section trajectories at quasisharp and non-
sharp intermediate split for the equimolar pentane(1)-
hexane(2)-heptane(3)-octane(4) mixture for L/V = 1.3(L/
V) sh , (L/V) sh = 0.614, x f −1 = x ∞ + 0.3 x sh ,η D = η B =
min min f −1 f −1
0.999; 0.99; 0.95; 0.90, separatrix sharp split section regions
3,4 1,2
R
Reg sep,r and Reg R sep,s are shaded (a); normal proection to face
1,2 3,4
1-2-3, (1) − η D = η B = 0.999, (2) − η D = η B = 0.9 (b).
sharp separation (at η D = η B = 0.999), calculation trajectories of sections come
1
1
close to points S and S , and at nonsharp separation they are far from them.
r s
Correspondingly, at sharp separation the necessary tray number is big, and at
nonsharp separation it is small.
The other projection at Fig. 7.5b shows two of these trajectories at η = 0.999
and η = 0.9. This projection makes it quite clear that at different purity values
the points x f−1 and x f are different: with a decrease of purity, these points move
3,4 1,2
away from separatrix surfaces for sharp split Reg R and Reg R , and they go
sep,r sep,s
1,2 3,4 3,4 1,2
deep into working trajectory bundles of the sections Reg R and Reg R . Table 7.1
w,r w,s
1,2 3,4