Page 63 - Distillation theory
P. 63
P1: FCH/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: VINOD/IYP T1: FCH
0521820928c02 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 17:58
2.10 Mixtures with Limited and Unlimited Separability 37
a) b) 1 y 1
B T
B x
5 1
2
3
F x
D T 4
x 1
0 x B x F x D 1
x D
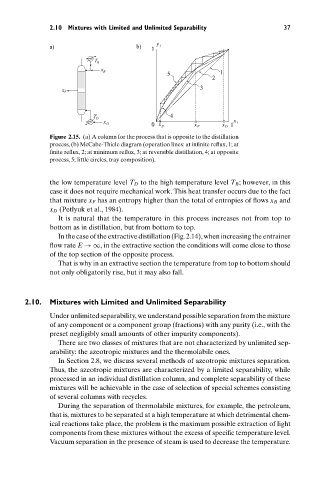
Figure 2.15. (a) A column for the process that is opposite to the distillation
process, (b) McCabe-Thiele diagram (operation lines: at infinite reflux, 1; at
finite reflux, 2; at minimum reflux, 3; at reversible distillation, 4; at opposite
process, 5; little circles, tray composition).
the low temperature level T D to the high temperature level T B ; however, in this
case it does not require mechanical work. This heat transfer occurs due to the fact
that mixture x F has an entropy higher than the total of entropies of flows x B and
x D (Petlyuk et al., 1984).
It is natural that the temperature in this process increases not from top to
bottom as in distillation, but from bottom to top.
Inthecaseoftheextractivedistillation(Fig.2.14),whenincreasingtheentrainer
flow rate E →∞, in the extractive section the conditions will come close to those
of the top section of the opposite process.
That is why in an extractive section the temperature from top to bottom should
not only obligatorily rise, but it may also fall.
2.10. Mixtures with Limited and Unlimited Separability
Under unlimited separability, we understand possible separation from the mixture
of any component or a component group (fractions) with any purity (i.e., with the
preset negligibly small amounts of other impurity components).
There are two classes of mixtures that are not characterized by unlimited sep-
arability: the azeotropic mixtures and the thermolabile ones.
In Section 2.8, we discuss several methods of azeotropic mixtures separation.
Thus, the azeotropic mixtures are characterized by a limited separability, while
processed in an individual distillation column, and complete separability of these
mixtures will be achievable in the case of selection of special schemes consisting
of several columns with recycles.
During the separation of thermolabile mixtures, for example, the petroleum,
that is, mixtures to be separated at a high temperature at which detrimental chem-
ical reactions take place, the problem is the maximum possible extraction of light
components from these mixtures without the excess of specific temperature level.
Vacuum separation in the presence of steam is used to decrease the temperature.