Page 119 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 119
92 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
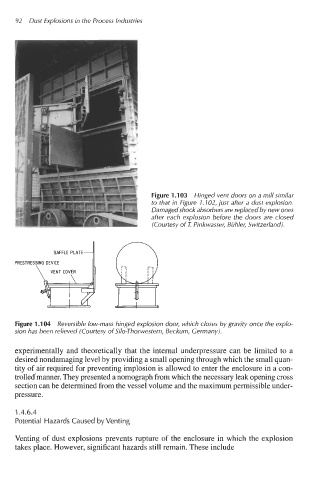
Figure 1 .I 03 Hinged vent doors on a mill similar
to that in Figure 1.102, just after a dust explosion.
Damaged shock absorbers are replaced by new ones
after each explosion before the doors are closed
(Courtesy of T. Pinkwasser, Biihler, Switzerland).
BAFFLE PLATE
Figure 1 .I 04 Reversible low-mass hinged explosion door, which closes by gravity once the explo-
sion has been relieved (Courtesy of Silo-Thorwestern, Beckurn, Germany).
experimentally and theoretically that the internal underpressure can be limited to a
desired nondamaging level by providing a small opening through which the small quan-
tity of air required for preventing implosion is allowed to enter the enclosure in a con-
trolled'manner. They presented a nomograph from which the necessary leak opening cross
section can be determined from the vessel volume and the maximum permissible under-
pressure.
1 A.6.4
Potential Hazards Caused by Venting
Venting of dust explosions prevents rupture of the enclosure in which the explosion
takes place. However, significant hazards still remain. These include