Page 300 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 300
Propagation of Flames in Dust Clouds 269
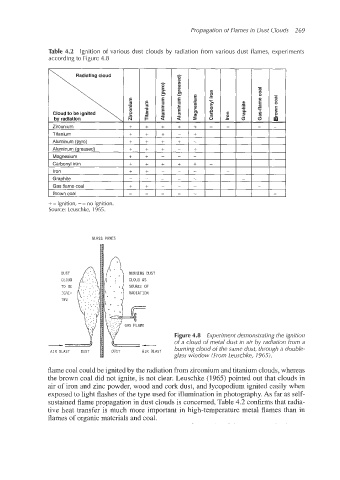
Table 4.2 Ignition of various dust clouds by radiation from various dust flames, experiments
according to Figure 4.8
-
.-s .-s .- m 8
c0
c
E
r
P
e
Cloud to be ignited \ 5 c .e c
E
R
F
by radiation - - (3
Zirconium + + + + I
Titanium + t + +
+
Aluminum (pyro) -
Aluminum (greased) I
Magnesium + +
Carbonvl iron + + + t t
Iron
Graphite
Gas flame coal + t
Brown coai
+ = ignition, -= no ignition.
Source: Leuschke, 1965.
GLASS PANES
BURNING DUST
Figure 4.8 Experiment demonstrating the ignition
of a cloud of metal dust in air by radiation from a
burning cloud of the same dust, through a double-
I
AIR BLAST
AIR BLAST DUST AIR BLAST
glass window (From Leuschke, 1965).
flame coal could be ignited by the radiation from zirconium and titanium clouds,whereas
the brown coal did not ignite, is not clear. Leuschke (1965) pointed out that clouds in
air of iron and zinc powder, wood and cork dust, and lycopodium ignited easily when
exposed to light flashes of the type used for illumination in photography. As far as self-
sustained flame propagation in dust clouds is concerned, Table 4.2 confirms that radia-
tive heat transfer is much more important in high-temperature metal flames than in
flames of organic materials and coal.