Page 426 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 426
Ignition of Dust Clouds and Dust Deposits 393
5.2.2.4
Ignition of Dust Layers by a Small, Electrically Heated Wire Coil Source:
Propagation of Smoldering Combustion in Dust Layers
Leisch, Kauffman, and Sichel(l984) studied ignition and smouldering combustion prop-
agation of dust layers in a wind tunnel where the top surface of the dust layer could be
subjected to a controlled air flow.
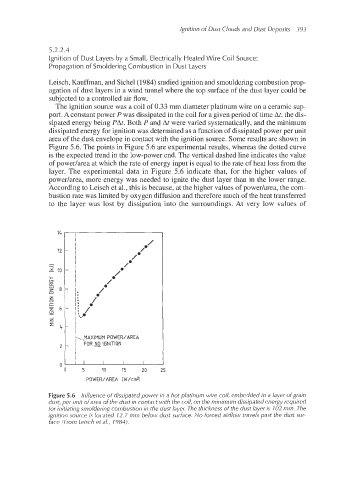
The ignition source was a coil of 0.33 mm diameter platinum wire on a ceramic sup-
port. A constant power P was dissipated in the coil for a given period of time At, the dis-
sipated energy being Pat. Both P and At were varied systematically, and the minimum
dissipated energy for ignition was determined as a function of dissipated power per unit
area of the dust envelope in contact with the ignition source. Some results are shown in
Figure 5.6. The points in Figure 5.6 are experimental results, whereas the dotted curve
is the expected trend in the low-power end. The vertical dashed line indicates the value
of power/area at which the rate of energy input is equal to the rate of heat loss from the
layer. The experimental data in Figure 5.6 indicate that, for the higher values of
Ipowedarea, more energy was needed to ignite the dust layer than in the lower range.
According to Leisch et al., this is because, at the higher values of powedarea, the com-
bustion rate was limited by oxygen diffusion and therefore much of the heat transferred
to the layer was lost by dissipation into the surroundings. At very low values of
+.MAXIMUM POWERIAREA
FOR IGNITION
0 5 10 15 20 25
POWER/AREA [W/crnZl
Figure 5.5 Influence of dissipated power in a hot platinum wire coil, embedded in a layer of grain
dust, per unit of area of the dust in contact with the coil, on the minimum dissipated energy required
Sor initiating smoldering combustion in the dust layer. The thickness of the dust layer is 702 mm. The
ignition source is located 12.7 mm below dust surface. No forced airflow travels past the dust sur-
face (From Leisch et al., 7984).