Page 96 - Dynamic Loading and Design of Structures
P. 96
Page 73
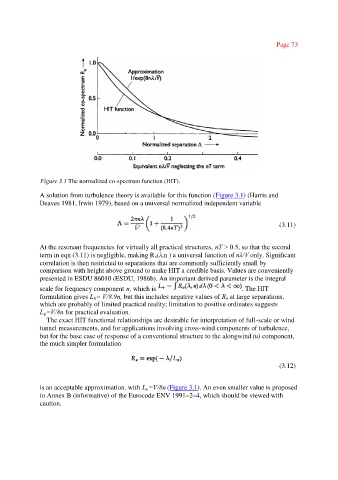
Figure 3.1 The normalized co-spectrum function (HIT).
A solution from turbulence theory is available for this function (Figure 3.1) (Harris and
Deaves 1981, Irwin 1979), based on a universal normalized independent variable
(3.11)
At the resonant frequencies for virtually all practical structures, nT > 0.5, so that the second
/
term in eqn (3.11) is negligible, making Ru(λ,n ) a universal function of nλV only. Significant
correlation is then restricted to separations that are commonly sufficiently small by
comparison with height above ground to make HIT a credible basis. Values are conveniently
presented in ESDU 86010 (ESDU, 1986b). An important derived parameter is the integral
scale for frequency component n, which is . The HIT
formulation gives Ln= V/8.9n, but this includes negative values of Ru at large separations,
which are probably of limited practical reality; limitation to positive ordinates suggests
L =V/8n for practical evaluation.
n
The exact HIT functional relationships are desirable for interpretation of full-scale or wind
tunnel measurements, and for applications involving cross-wind components of turbulence,
but for the base case of response of a conventional structure to the alongwind (u) component,
the much simpler formulation
(3.12)
is an acceptable approximation, with L =V/8n (Figure 3.1). An even smaller value is proposed
n
in Annex B (informative) of the Eurocode ENV 1991–2–4, which should be viewed with
caution.