Page 52 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 52
4.6 Sinusoidal reactivity and frequency response 43
0.015
0.01
0.005
ΔP/P(0) 0
−0.005
−0.01
−0.015
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Time (s)
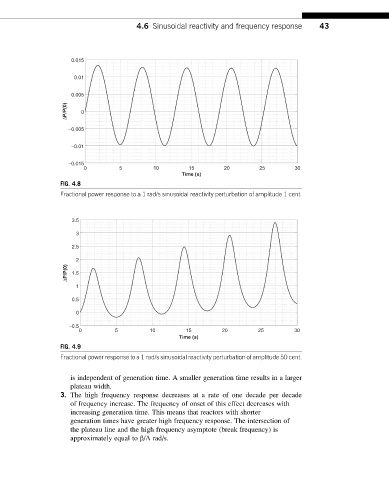
FIG. 4.8
Fractional power response to a 1 rad/s sinusoidal reactivity perturbation of amplitude 1 cent.
3.5
3
2.5
2
ΔP/P(0) 1.5
1
0.5
0
−0.5
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Time (s)
FIG. 4.9
Fractional power response to a 1 rad/s sinusoidal reactivity perturbation of amplitude 50 cent.
is independent of generation time. A smaller generation time results in a larger
plateau width.
3. The high frequency response decreases at a rate of one decade per decade
of frequency increase. The frequency of onset of this effect decreases with
increasing generation time. This means that reactors with shorter
generation times have greater high frequency response. The intersection of
the plateau line and the high frequency asymptote (break frequency) is
approximately equal to β/Λ rad/s.