Page 44 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 44
M01_CHAF9601_04_SE_C01.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:02 Page 11
Chapter 1 Introduction to e-business and e-commerce 11
The UK government also used a broad definition when explaining the scope of e-commerce
to industry:
E-commerce is the exchange of information across electronic networks, at any stage in
the supply chain, whether within an organization, between businesses, between busi-
nesses and consumers, or between the public and private sector, whether paid or unpaid.
(Cabinet Office, 1999)
These definitions show that electronic commerce is not solely restricted to the actual buying and
selling of products, but also includes pre-sale and post-sale activities across the supply chain.
E-commerce is facilitated by a range of digital technologies that enable electronic communi-
cations. These technologies include Internet communications through web sites and e-mail as
well as other digital media such as wireless or mobile and media for delivering digital television
such as cable and satellite. We will explain the characteristics of these technologies and some of
the challenges in managing them in Chapter 3.
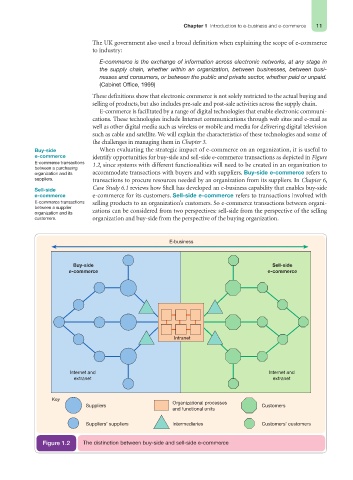
Buy-side When evaluating the strategic impact of e-commerce on an organization, it is useful to
e-commerce identify opportunities for buy-side and sell-side e-commerce transactions as depicted in Figure
E-commerce transactions 1.2, since systems with different functionalities will need to be created in an organization to
between a purchasing
organization and its accommodate transactions with buyers and with suppliers. Buy-side e-commerce refers to
suppliers. transactions to procure resources needed by an organization from its suppliers. In Chapter 6,
Case Study 6.1 reviews how Shell has developed an e-business capability that enables buy-side
Sell-side
e-commerce e-commerce for its customers. Sell-side e-commerce refers to transactions involved with
E-commerce transactions selling products to an organization’s customers. So e-commerce transactions between organi-
between a supplier
organization and its zations can be considered from two perspectives: sell-side from the perspective of the selling
customers. organization and buy-side from the perspective of the buying organization.
E-business
Buy-side Sell-side
e-commerce e-commerce
Intranet
Internet and Internet and
extranet extranet
Key
Organizational processes
Suppliers Customers
and functional units
Suppliers’ suppliers Intermediaries Customers’ customers
Figure 1.2 The distinction between buy-side and sell-side e-commerce