Page 203 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 203
CHAPTER 10 • Orbital-Scale Changes in Carbon Dioxide and Methane 179
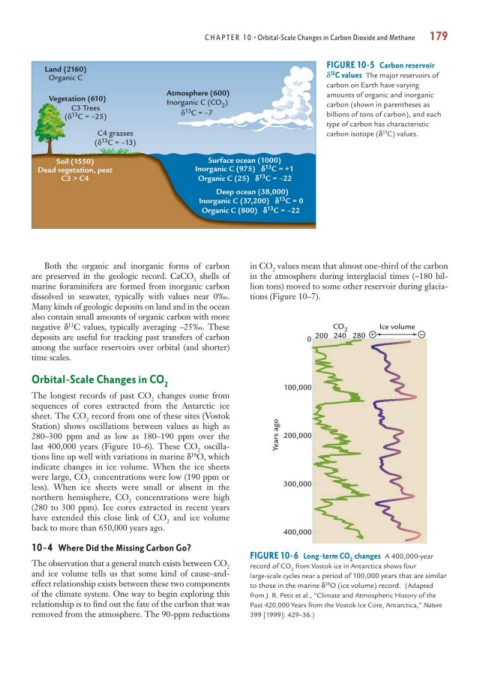
FIGURE 10-5 Carbon reservoir
Land (2160) 13
Organic C δ C values The major reservoirs of
carbon on Earth have varying
Atmosphere (600) amounts of organic and inorganic
Vegetation (610)
Inorganic C (CO ) carbon (shown in parentheses as
C3 Trees 13 2
13
(δ C = –25) δ C = –7 billions of tons of carbon), and each
type of carbon has characteristic
13
C4 grasses carbon isotope (δ C) values.
13
(δ C = –13)
Soil (1550) Surface ocean (1000)
13
Dead vegetation, peat Inorganic C (975) δ C = +1
13
C3 > C4 Organic C (25) δ C = –22
Deep ocean (38,000)
13
Inorganic C (37,200) δ C = 0
13
Organic C (800) δ C = –22
Both the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in CO values mean that almost one-third of the carbon
2
are preserved in the geologic record. CaCO shells of in the atmosphere during interglacial times (~180 bil-
3
marine foraminifera are formed from inorganic carbon lion tons) moved to some other reservoir during glacia-
dissolved in seawater, typically with values near 0‰. tions (Figure 10–7).
Many kinds of geologic deposits on land and in the ocean
also contain small amounts of organic carbon with more
13
negative δ C values, typically averaging –25‰. These CO 2 Ice volume _
deposits are useful for tracking past transfers of carbon 0 200 240 280 +
among the surface reservoirs over orbital (and shorter)
time scales.
Orbital-Scale Changes in CO
2 100,000
The longest records of past CO changes come from
2
sequences of cores extracted from the Antarctic ice
sheet. The CO record from one of these sites (Vostok
2
Station) shows oscillations between values as high as
280–300 ppm and as low as 180–190 ppm over the Years ago 200,000
last 400,000 years (Figure 10–6). These CO oscilla-
2
18
tions line up well with variations in marine δ O, which
indicate changes in ice volume. When the ice sheets
were large, CO concentrations were low (190 ppm or
2
less). When ice sheets were small or absent in the 300,000
northern hemisphere, CO concentrations were high
2
(280 to 300 ppm). Ice cores extracted in recent years
have extended this close link of CO and ice volume
2
back to more than 650,000 years ago.
400,000
10-4 Where Did the Missing Carbon Go?
FIGURE 10-6 Long-term CO changes A 400,000-year
2
The observation that a general match exists between CO
2 record of CO from Vostok ice in Antarctica shows four
2
and ice volume tells us that some kind of cause-and- large-scale cycles near a period of 100,000 years that are similar
effect relationship exists between these two components to those in the marine δ O (ice volume) record. (Adapted
18
of the climate system. One way to begin exploring this from J. R. Petit et al., “Climate and Atmospheric History of the
relationship is to find out the fate of the carbon that was Past 420,000 Years from the Vostok Ice Core, Antarctica,” Nature
removed from the atmosphere. The 90-ppm reductions 399 [1999]: 429–36.)