Page 230 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 230
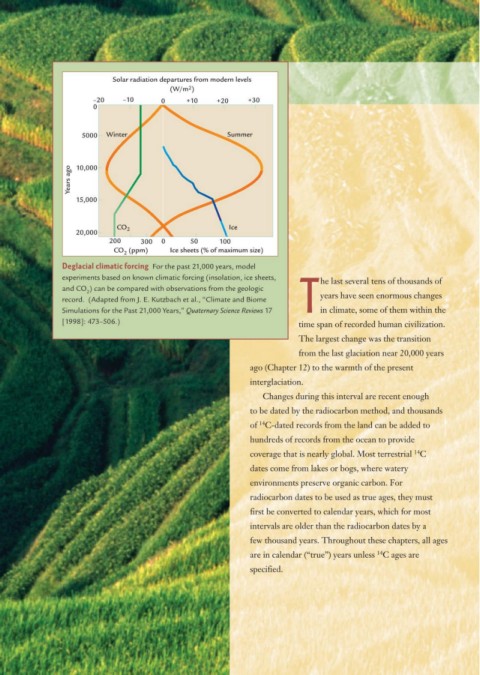
Solar radiation departures from modern levels
(W/m 2 )
–20 –10 0 +10 +20 +30
0
5000 Winter Summer
Years ago 10,000
15,000
CO 2 Ice
20,000
200 300 0 50 100
CO (ppm) Ice sheets (% of maximum size)
2
Deglacial climatic forcing For the past 21,000 years, model
experiments based on known climatic forcing (insolation, ice sheets,
he last several tens of thousands of
and CO ) can be compared with observations from the geologic
2 years have seen enormous changes
record. (Adapted from J. E. Kutzbach et al., “Climate and Biome
Simulations for the Past 21,000 Years,” Quaternary Science Reviews 17 Tin climate, some of them within the
[1998]: 473–506.) time span of recorded human civilization.
The largest change was the transition
from the last glaciation near 20,000 years
ago (Chapter 12) to the warmth of the present
interglaciation.
Changes during this interval are recent enough
to be dated by the radiocarbon method, and thousands
14
of C-dated records from the land can be added to
hundreds of records from the ocean to provide
14
coverage that is nearly global. Most terrestrial C
dates come from lakes or bogs, where watery
environments preserve organic carbon. For
radiocarbon dates to be used as true ages, they must
first be converted to calendar years, which for most
intervals are older than the radiocarbon dates by a
few thousand years. Throughout these chapters, all ages
14
are in calendar (“true”) years unless C ages are
specified.